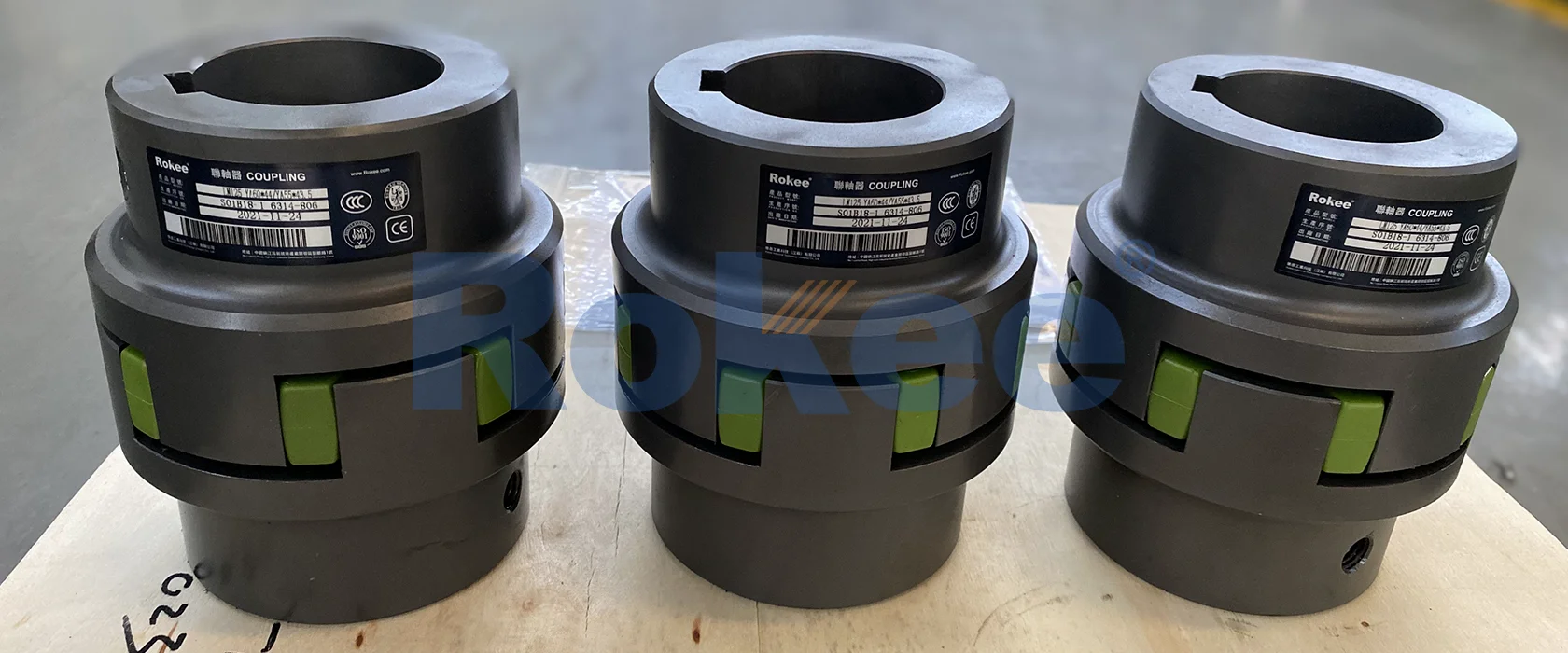

Rokee is a well-known high-quality supplier of Flexible Jaw Couplings and technical services in China, customize flexible jaw couplings according to user drawings, alternatively, if the user provides flexible jaw couplings parameters, we can select the model and design drawings for you, support wholesale and export.


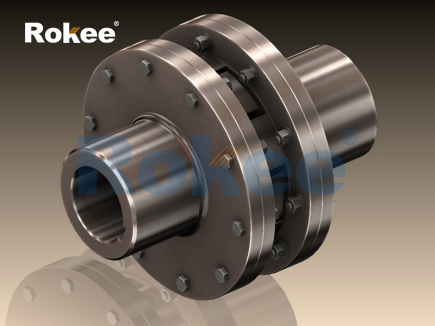

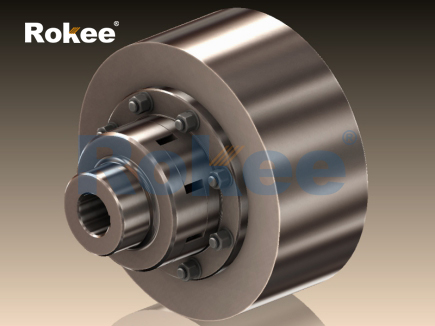


In the realm of mechanical power transmission, couplings play a pivotal role in connecting rotating shafts, enabling efficient torque transfer while mitigating the adverse effects of shaft misalignment, vibration, and shock loads. Among the diverse array of coupling technologies, the flexible jaw coupling stands out as one of the most widely used solutions in industrial, commercial, and automotive applications. Characterized by its split jaw-shaped hubs and a central elastomeric insert (often referred to as a spider), this coupling type combines simplicity of design with effective flexibility, making it ideal for medium to low-torque power transmission systems. Unlike rigid couplings that demand precise shaft alignment or complex metallic flexible couplings, the flexible jaw coupling leverages the elastic deformation of its spider element to accommodate misalignments and dampen vibrations. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of flexible jaw couplings, exploring their fundamental working principles, structural components, material selection criteria, key performance advantages, typical application scenarios, and essential maintenance practices, thereby offering a holistic understanding of their role in enhancing the reliability and efficiency of mechanical systems.
The core functionality of a flexible jaw coupling lies in its ability to transmit torque from a driving shaft to a driven shaft while compensating for three primary types of shaft misalignment: angular misalignment (where the shafts intersect at an angle), parallel misalignment (where the shafts are radially offset), and axial misalignment (where the shafts move longitudinally toward or away from each other). This functionality is made possible by the coupling’s distinctive design, which consists of two jaw-shaped hubs and a central elastomeric spider that fits snugly between the jaws of the two hubs.
When torque is applied to the driving shaft, the force is transmitted through the driving hub to the spider. The spider, fabricated from elastic material, deforms elastically to accommodate any existing misalignment between the two shafts, ensuring that torque is smoothly transferred to the driven hub and subsequent shaft. The jaw design of the hubs is critical to this process, as the interlocking teeth of the hubs and the spider create a secure connection that prevents slippage during torque transmission. Unlike couplings with sliding components, the flexible jaw coupling operates with minimal backlash, ensuring precise torque transfer in applications requiring moderate positional accuracy.
Another key principle of flexible jaw coupling operation is its vibration damping capability. The elastomeric spider acts as a shock absorber, absorbing and dissipating vibrational energy generated during system startup, shutdown, or variable load operations. This damping effect helps to reduce noise levels and protect sensitive components such as bearings, gears, and shafts from premature wear caused by excessive mechanical stress. Additionally, the spider’s elasticity provides a degree of torsional flexibility, which helps to reduce torsional vibrations and improve the overall stability of the power transmission system, particularly in applications with variable speed or load fluctuations.
Flexible jaw couplings also operate without the need for complex lubrication systems. The elastomeric spider’s contact with the hub jaws is designed to minimize friction, and the materials used for the spider are inherently resistant to wear under normal operating conditions. This eliminates the risk of lubricant leakage, contamination, and the associated maintenance costs, making the coupling suitable for applications where clean operation is a priority.
Flexible jaw couplings feature a simple yet robust structure, consisting of three primary components: two jaw hubs, an elastomeric spider, and fastening hardware. Each component is engineered to work in synergy to ensure reliable torque transmission, misalignment compensation, and long-term operational stability.
The jaw hubs are the primary load-bearing components of the coupling, responsible for connecting the coupling to the driving and driven shafts. Typically manufactured from high-strength materials such as cast iron, carbon steel, aluminum alloy, or even plastic (for light-duty applications), the hubs are designed with a series of evenly spaced jaws (or teeth) around their circumference. The number of jaws varies depending on the coupling’s size and torque capacity, with larger couplings typically featuring more jaws to distribute the load evenly. The choice of hub material is influenced by the application’s torque requirements, weight constraints, and environmental conditions. For example, cast iron hubs are preferred for cost-sensitive, medium-torque applications, while carbon steel hubs are used for higher-torque scenarios requiring greater strength. Aluminum alloy hubs are selected for lightweight applications such as portable machinery or automotive systems, where weight reduction is essential. Plastic hubs, made from materials such as nylon or polypropylene, are used for light-duty applications with low torque requirements, such as small electric motors or household appliances.
Hubs are typically designed with standard connection features to ensure secure attachment to the shafts. Common connection methods include keyway fittings, set screws, compression couplings, or tapered bushings. Keyway fittings are the most widely used, as they provide a secure, slip-free connection by engaging a key inserted into grooves (keyways) machined into both the hub and the shaft. Set screws are used for lighter-duty applications, where the screw is tightened against the shaft to prevent rotation. Compression couplings and tapered bushings are preferred for applications requiring quick installation and removal without shaft modification, as they use a clamping mechanism to secure the hub to the shaft.
The elastomeric spider is the defining component of the flexible jaw coupling, responsible for providing flexibility, misalignment compensation, and vibration damping. Spiders are typically fabricated from rubber or synthetic elastomers and are designed with a series of lobes (or arms) that match the number of jaws on the hubs. The lobes fit snugly into the spaces between the jaws, creating a secure interlock that transmits torque while allowing for elastic deformation. Spiders are available in two primary designs: solid spiders and split spiders. Solid spiders are one-piece structures, offering maximum torque transmission capability but requiring the entire coupling to be disassembled for replacement. Split spiders, on the other hand, are designed in two or more segments, allowing for easy replacement without disassembling the hubs or shafts—a significant advantage for applications where downtime must be minimized.
Fastening hardware, such as bolts, nuts, and washers, is used to secure the two hubs together, ensuring that the spider remains properly seated between the jaws. In some designs, the hubs are bolted directly together, with the spider held in place by the compression between the two sets of jaws. In other designs, the spider is secured to the hubs using small bolts or pins. These fasteners are typically made from high-strength steel to ensure they can withstand the tensile forces generated during operation. Proper torquing of the fasteners is critical to maintaining the coupling’s integrity, as loose fasteners can lead to excessive vibration, noise, and premature failure of the spider.
The performance, durability, and suitability of a flexible jaw coupling for a specific application are heavily dependent on the materials used for its components—particularly the elastomeric spider. Material selection is influenced by a range of factors, including operating temperature, torque requirements, environmental conditions (such as exposure to chemicals, oil, or moisture), and the level of vibration damping needed.
For the elastomeric spider, the most commonly used materials are natural rubber and synthetic elastomers. Natural rubber is preferred for general-purpose applications due to its excellent elasticity, resilience, and low cost. It performs well in moderate temperature ranges (typically -20°C to 80°C) and offers good resistance to wear and tear under normal operating conditions. However, natural rubber has limited resistance to oil, chemicals, and ozone, making it unsuitable for harsh environments.
Synthetic elastomers are used for applications requiring enhanced performance characteristics. Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a popular choice for applications involving exposure to oil or petroleum products, as it offers excellent oil resistance. It also provides good elasticity and wear resistance, making it suitable for use in industrial machinery such as pumps, compressors, and hydraulic systems. Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber is preferred for applications exposed to ozone, weathering, or high temperatures (up to 120°C). It offers excellent resistance to UV radiation, moisture, and chemicals, making it ideal for outdoor applications such as agricultural machinery or renewable energy systems.
For high-temperature applications (exceeding 120°C) or environments with aggressive chemicals, silicone rubber or fluorinated elastomers (such as Viton) are used. Silicone rubber can withstand temperatures up to 200°C and offers good resistance to ozone and weathering, but it has limited oil resistance. Fluorinated elastomers provide exceptional resistance to chemicals, oil, and high temperatures (up to 250°C), making them suitable for specialized applications such as chemical processing or high-temperature industrial furnaces, although they are more costly than other elastomers.
The jaw hubs and fasteners are typically made from materials selected for their strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. Cast iron (such as GG25 or GG30) is widely used for hubs in general-purpose applications due to its low cost and good machinability. Carbon steel (such as 45# steel) is used for higher-torque applications requiring greater strength, while stainless steel (such as 304 or 316) is selected for applications in corrosive environments, such as marine or food processing industries. Plastic hubs, made from nylon or polypropylene, are used for light-duty applications with low torque requirements. Fasteners are usually made from high-strength carbon steel or stainless steel, with stainless steel fasteners being preferred for corrosive environments to prevent rust and degradation.
Flexible jaw couplings offer a range of performance advantages that make them a preferred choice for numerous industrial, agricultural, commercial, and automotive applications. These advantages include effective misalignment compensation, excellent vibration damping, simple installation and maintenance, cost-effectiveness, and versatility.
One of the most significant advantages of flexible jaw couplings is their ability to compensate for moderate levels of shaft misalignment. They can typically accommodate angular misalignment of up to 1-2 degrees, parallel misalignment of 0.5-2 millimeters, and axial misalignment of several millimeters—sufficient for most medium to low-torque applications. This misalignment compensation capability reduces the need for precise shaft alignment during installation, simplifying the setup process and reducing installation time and costs. It also helps to reduce stress on shafts, bearings, and other mechanical components, extending their service life and minimizing the risk of premature failure.
The elastomeric spider provides excellent vibration damping and shock absorption, making flexible jaw couplings ideal for applications with variable loads, frequent startups/shutdowns, or high levels of operational vibration. The spider absorbs and dissipates vibrational energy, reducing noise levels and protecting sensitive components from damage caused by shock loads. This is particularly beneficial in applications such as pumps, compressors, electric motors, and machine tools, where vibration can significantly impact performance and component life.
Flexible jaw couplings are also renowned for their simple installation and maintenance requirements. Their straightforward structure consists of only a few components, making installation quick and easy. Unlike gear couplings or universal joints, they do not require complex lubrication systems, eliminating the need for regular lubrication checks and refills. Additionally, split spider designs allow for easy replacement of the spider without disassembling the entire coupling or removing the shafts, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. This ease of maintenance is a key advantage for applications where operational continuity is critical, such as in manufacturing plants or processing facilities.
Cost-effectiveness is another major benefit of flexible jaw couplings. Compared to metallic flexible couplings (such as diaphragm or disc couplings) or complex elastomeric couplings, flexible jaw couplings are typically more affordable to manufacture and purchase. Their low maintenance requirements further reduce long-term operational costs, making them an attractive option for cost-sensitive applications such as small to medium-sized industrial machinery, agricultural equipment, and commercial HVAC systems.
Finally, flexible jaw couplings are highly versatile, with a wide range of sizes and configurations available to suit different torque requirements, shaft diameters, and application needs. They can be customized with different hub materials, spider materials, and connection methods to adapt to specific operating conditions, from light-duty household appliances to heavy-duty industrial machinery. This versatility makes them a universal solution for many power transmission applications.
Due to their unique combination of advantages—including effective misalignment compensation, vibration damping, simple maintenance, cost-effectiveness, and versatility—flexible jaw couplings are used in a wide range of applications across various industries. They are particularly well-suited for medium to low-torque applications requiring reliable torque transmission with minimal maintenance.
In the industrial sector, flexible jaw couplings are commonly used in pumps, compressors, fans, blowers, electric motors, and machine tools. In pump applications, they compensate for misalignment between the motor and pump shafts, reducing stress on the pump’s bearings and impeller. Their vibration damping capability helps to minimize noise and extend the service life of the pump and motor. Similarly, in compressors and fans, the couplings absorb shock loads during startup and reduce operational vibrations, ensuring smooth and efficient performance. Electric motors, particularly those used in small to medium-sized industrial machinery, benefit from the coupling’s ability to accommodate minor misalignments and reduce torsional vibrations. In machine tools such as lathes, milling machines, and drilling machines, the coupling’s minimal backlash ensures precise torque transmission, contributing to accurate machining operations.
The agricultural industry relies on flexible jaw couplings for use in tractors, harvesters, irrigation pumps, and other farm machinery. Agricultural equipment often operates in harsh, uneven terrain, leading to significant shaft misalignment and shock loads. The flexible jaw coupling’s ability to absorb these misalignments and dampen shocks makes it ideal for these applications. Additionally, the coupling’s simple maintenance requirements are well-suited for agricultural settings, where access to specialized maintenance equipment may be limited. The use of corrosion-resistant materials (such as stainless steel hubs and EPDM spiders) ensures reliable operation in outdoor, wet, or dusty agricultural environments.
In the commercial and building services sector, flexible jaw couplings are used in HVAC systems, air handlers, water circulation pumps, and refrigeration units. HVAC systems require reliable, low-maintenance components to ensure continuous operation, and the flexible jaw coupling’s simple design and lack of lubrication requirements make it an ideal choice. Its vibration damping capability helps to reduce noise levels in commercial buildings, improving indoor air quality and comfort. Water circulation pumps and refrigeration units benefit from the coupling’s misalignment compensation, which reduces wear on pump components and extends service life.
The automotive and transportation industry uses flexible jaw couplings in a range of applications, including small electric vehicles, forklifts, conveyor systems, and automotive auxiliary components (such as water pumps and alternators). In small electric vehicles and forklifts, the coupling’s lightweight design (when using aluminum alloy or plastic hubs) helps to reduce overall vehicle weight, improving energy efficiency. Its vibration damping capability also enhances driver comfort by reducing noise and vibration transmitted to the vehicle’s chassis. Conveyor systems, which are widely used in manufacturing and logistics, benefit from the coupling’s ability to accommodate misalignment between the motor and conveyor drive shafts, ensuring smooth and reliable material transport.
Specialized applications for flexible jaw couplings include marine equipment (such as small boat engines, auxiliary pumps, and winches), where corrosion resistance is critical, and renewable energy systems (such as small wind turbines and solar water pumps), where the coupling’s ability to operate in outdoor environments and dampen vibrations is essential. In these applications, the use of EPDM or silicone rubber spiders ensures resistance to weathering, ozone, and moisture, while stainless steel hubs provide corrosion resistance. Additionally, flexible jaw couplings are used in household appliances such as washing machines, dryers, and air conditioners, where their compact size, low noise, and reliability make them ideal for light-duty power transmission.
While flexible jaw couplings are low-maintenance components, proper maintenance is essential to ensure their reliable operation, extend their service life, and prevent unexpected downtime. The key maintenance practices for flexible jaw couplings include regular inspection, proper installation, spider replacement, and monitoring of operating conditions.
Regular inspection is the cornerstone of effective maintenance for flexible jaw couplings. Inspections should be conducted periodically—typically every 3-6 months, depending on the application and operating conditions—to check for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. During inspection, the spider should be examined for cracks, tears, hardening, or excessive deformation, which are indicators of material degradation. The hubs and fasteners should be checked for tightness, corrosion, or damage. Loose fasteners should be tightened immediately to prevent vibration and potential failure. Additionally, the coupling should be inspected for excessive vibration or noise during operation, which may indicate misalignment, worn components, or improper installation. It is also important to check for any signs of spider displacement or uneven wear, which may indicate misalignment beyond the coupling’s rated capacity.
Proper installation is critical to the performance and service life of flexible jaw couplings. During installation, the shafts should be aligned as accurately as possible to minimize the amount of misalignment the coupling must accommodate. While the coupling can compensate for moderate misalignment, operating beyond its rated misalignment limits will accelerate wear on the spider and reduce its service life. The hubs should be securely attached to the shafts using the appropriate connection method (keyway, set screws, compression coupling, or tapered bushing), and the fasteners should be torqued to the manufacturer’s specifications. It is also important to ensure that the spider is properly seated between the hub jaws to prevent uneven loading and premature failure.
Spider replacement is a key maintenance task for flexible jaw couplings. The service life of the spider depends on the operating conditions, including temperature, load, misalignment, and environmental factors. As a general guideline, spiders should be replaced every 1-3 years, or sooner if signs of wear or damage are detected. When replacing the spider, it is important to use a replacement spider that is compatible with the coupling’s design and specifications, including the correct material, size, and number of lobes. Split spiders can be replaced without disassembling the hubs or shafts, simplifying the replacement process and minimizing downtime. Solid spiders require the coupling to be disassembled, so it is recommended to schedule this maintenance during planned shutdowns.
Monitoring of operating conditions is essential to prevent premature failure of flexible jaw couplings. The coupling should be operated within its rated torque, speed, and temperature limits. Exceeding these limits can cause excessive stress on the spider and hubs, leading to premature wear or failure. Additionally, the operating environment should be monitored for exposure to chemicals, oil, or moisture, which can degrade the spider. If the coupling is used in a corrosive environment, regular cleaning and inspection of the hubs and fasteners are recommended to prevent corrosion. It is also important to avoid overheating the coupling, as high temperatures can accelerate the degradation of the elastomeric spider.
In addition to these maintenance practices, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for the specific coupling model. Manufacturers often provide detailed maintenance instructions, including recommended inspection intervals, torque specifications, and replacement parts. Adhering to these guidelines ensures that the coupling operates at peak performance and extends its service life.
Flexible jaw couplings have established themselves as a reliable, cost-effective, and versatile solution for power transmission in a wide range of applications. Their unique design, centered around jaw-shaped hubs and an elastomeric spider, provides effective misalignment compensation, vibration damping, and shock absorption—attributes that are critical for protecting mechanical components and ensuring smooth system operation. The selection of appropriate materials for the spider and hubs is key to optimizing the coupling’s performance for specific operating conditions, whether in industrial, agricultural, commercial, or specialized environments.
The key advantages of flexible jaw couplings—including simple installation, low maintenance requirements, cost-effectiveness, and versatility—make them an attractive choice for medium to low-torque applications where reliability and affordability are priorities. From industrial pumps and compressors to agricultural machinery, HVAC systems, and household appliances, these couplings play a vital role in ensuring the efficient and continuous operation of mechanical systems.
Proper maintenance, including regular inspection, proper installation, timely spider replacement, and monitoring of operating conditions, is essential to maximizing the service life of flexible jaw couplings and minimizing downtime. By following these maintenance practices and adhering to manufacturer guidelines, users can ensure that their flexible jaw couplings operate reliably for years to come.
As technology advances and industrial requirements evolve, flexible jaw couplings are likely to see further improvements in material performance and design optimization. The development of new synthetic elastomers with enhanced temperature resistance, chemical resistance, and durability will expand their application range, making them suitable for even more demanding environments. With their proven performance and versatility, flexible jaw couplings are poised to remain a key component in mechanical power transmission systems across industries for the foreseeable future.
« Flexible Jaw Couplings » Post Date: 2024/4/25 , https://www.rokeecoupling.net/tags/flexible-jaw-couplings.html