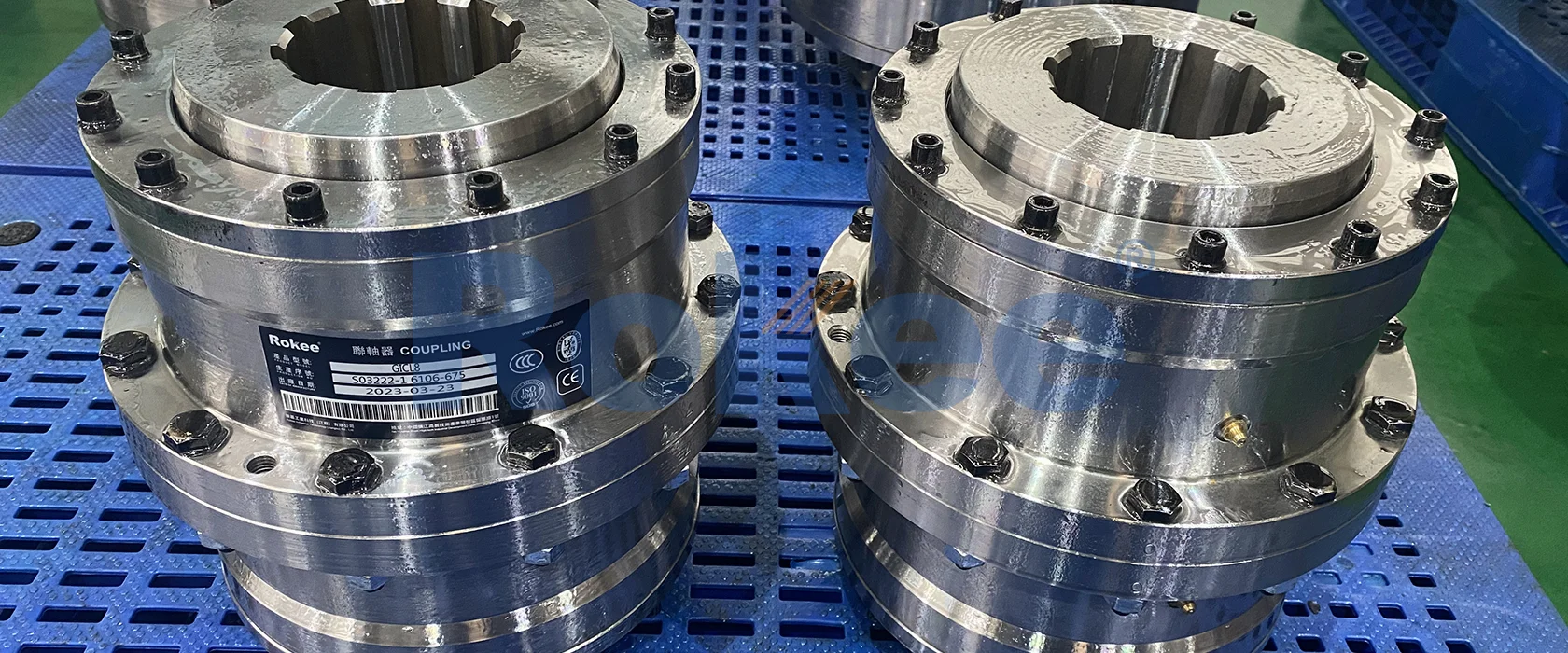

Rokee is a well-known high-quality supplier of Geared Couplings and technical services in China, customize geared couplings according to user drawings, alternatively, if the user provides geared couplings parameters, we can select the model and design drawings for you, support wholesale and export.
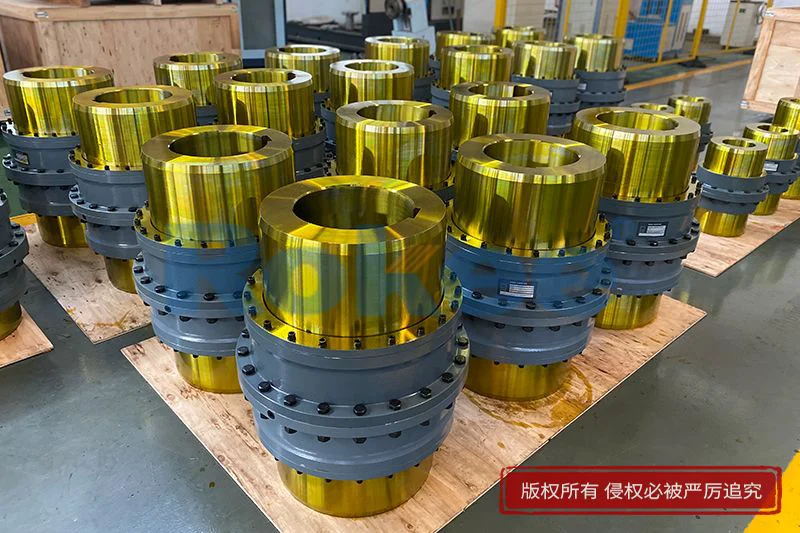








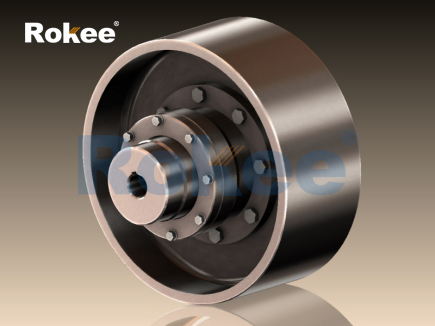




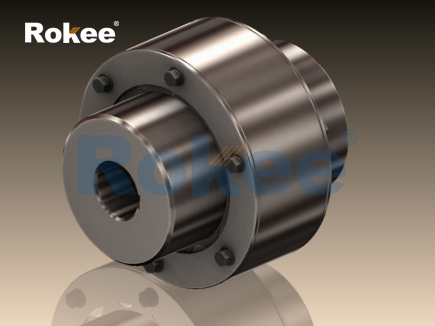



Geared coupling is a mechanical transmission device that transmits torque and motion through gear meshing, playing a crucial role in modern industrial transmission systems. This type of coupling consists of two sleeves with internal and external teeth, which connect the two shafts through gear meshing, allowing for a certain degree of axial, radial, and angular deviation compensation.
Compared with traditional rigid couplings, geared couplings have greater deviation compensation capabilities; Compared to elastic couplings, it can transmit greater torque. Its unique structural characteristics make it perform well under heavy loads, high speeds, or conditions where the shaft system is misaligned, making it the preferred transmission solution for many industrial applications.
The core working principle of geared couplings is based on the meshing characteristics of involute gears. A typical structure includes two external gear shaft sleeves and two internal gear rings. The external gear shaft sleeve is fixed to the drive shaft and the driven shaft through keyway or interference fit, while the internal gear ring is connected as a whole through bolts. The meshing of internal and external teeth not only transmits torque, but also allows for relative motion in all directions.
During the torque transmission process, the driving force is transmitted through the shaft to the outer gear sleeve, transmitted to the inner gear ring through gear meshing, and then transmitted to the driven shaft through the other side meshing. This design enables the coupling to compensate for various shaft system deviations: axial displacement is compensated through sliding of the tooth surface, radial displacement is adapted through backlash, and angular deviation is achieved through relative inclination of the tooth surface.
It is worth noting that the lubrication system of modern geared couplings is crucial to their performance. Most designs use grease lubrication or oil bath lubrication, and advanced models may be equipped with a circulating oil lubrication system, effectively reducing tooth wear and heat dissipation, significantly extending service life.
Standard geared coupling
The most common type consists of two outer toothed shaft sleeves and an intermediate sleeve with inner teeth. Suitable for transmission systems with medium precision requirements, the compensation capability is usually between ± 3-5mm in the axial direction, 0.4-1.5mm in the radial direction, and 1 ° -1.5 ° in the angular direction. This type of coupling is widely used in the field of general machinery.
High speed geared coupling
Specially designed for high-speed working conditions, using precision machined gear profiles and special balancing processes. Typical features include reduced weight, optimized tooth profile, and enhanced lubrication system. The speed can reach over 10000rpm and is used for equipment such as turbomachinery and centrifugal compressors.
Heavy duty geared coupling
The characteristics are high torque transmission ability, hardened tooth surface treatment, and a more robust overall structure. The torque range can reach millions of Newton meters, used in heavy industry fields such as metallurgical equipment, mining machinery, and ship propulsion systems.
Compact geared coupling
The ideal choice for space constrained environments, reducing axial dimensions through integrated design while maintaining good performance. Commonly found in precision equipment such as machine tools and robots, with relatively small compensation capabilities but higher accuracy.
Other special types include corrosion-resistant (stainless steel material), maintenance free (special sealing and lubrication), and universal geared couplings, which meet the specific needs of different industrial scenarios.
Geared couplings exhibit multiple outstanding characteristics in the field of mechanical transmission: their torque density is extremely high, and the torque they can transmit per unit size far exceeds that of most other types of couplings; The efficiency is usually between 98% and 99.5%, with minimal energy loss; A well-designed product can have a lifespan of tens of thousands of hours.
Compared with elastic couplings, geared couplings have higher stiffness and greater torsional stiffness, without elastic hysteresis, ensuring the accuracy of transmission. Compared with diaphragm couplings, it has stronger overload capacity and deviation tolerance. However, geared couplings generally require regular lubrication and maintenance, and the manufacturing cost is relatively high.
In practical applications, geared couplings exhibit excellent vibration damping characteristics, and the slight sliding generated during gear meshing can absorb some of the vibration energy, which helps protect other components of the transmission system. Meanwhile, modern design further enhances compensation capability and durability by optimizing tooth profiles, such as drum shaped teeth.
The correct selection of geared couplings requires consideration of multiple factors: firstly, torque requirements. Normal working torque and peak torque should be calculated, and a model with appropriate margin should be selected for the rated value; The speed range directly affects the balance requirements and heating situation of the coupling; The shaft diameter size determines the interface specifications; The deviation situation is related to the required compensation capability.
Environmental factors are equally important: temperature affects material properties and lubrication selection; Humidity and corrosive media determine the protection level requirements; Space constraints limit the external dimensions of the coupling. For special applications such as the food and pharmaceutical industry, designs that comply with hygiene standards may be necessary.
Suggested selection steps: 1) Determine application parameters; 2) Calculate equivalent torque; 3) Evaluate the deviation situation; 4) Consider environmental conditions; 5) Choose the appropriate type; 6) Check the size interface; 7) Confirm installation space. By utilizing the selection software or calculation tools provided by manufacturers, the accuracy of selection can be greatly improved.
The correct installation procedure is crucial for the performance of geared couplings. Firstly, the shaft end and coupling inner hole should be thoroughly cleaned, and the size fit should be checked; Use appropriate tools for assembly to avoid directly tapping the gear parts; Gradually and evenly tighten the connecting bolts to the specified torque; Finally, check the alignment to ensure that the deviation is within the allowable range.
Daily maintenance work mainly includes regularly checking the lubrication status, supplementing or replacing lubricants according to recommended cycles; Monitor the abnormal increase in operating temperature; Pay attention to abnormal noise or vibration; Regularly check the integrity of the seals. For critical equipment, condition monitoring techniques such as vibration analysis can be used to evaluate the health status of the coupling.
Common fault phenomena include: tooth surface wear (caused by insufficient lubrication or poor alignment), seal failure (resulting in lubrication leakage), abnormal vibration (possibly caused by severe misalignment or loose components), and bolt fracture (caused by overload or fatigue). Timely detection and handling of these issues can prevent more serious equipment damage.
Industrial manufacturing field
In the steel metallurgy industry, geared couplings are widely used in heavy equipment such as rolling mills and straightening machines; This type of coupling is also widely used in the transmission of drying drums in papermaking machinery to handle high torque while compensating for deviations caused by thermal expansion.
energy sector
The turbine generator set of the power plant uses high-performance geared couplings to connect the turbine and the generator; Special designed couplings are often used between the gearbox of wind turbines and the generator to adapt to the complex working conditions at the top of the tower.
transportation
In the ship propulsion system, geared couplings connect the diesel engine and propeller shaft, which can compensate for deviations caused by ship deformation; The transmission systems of some heavy vehicles and railway locomotives also adopt similar designs.
special application
In the fields of military equipment and aerospace, special geared couplings meet the reliable transmission requirements in extreme environments; The micro precision geared coupling in the robot joints achieves high-precision motion transmission in a compact space.
« Geared Couplings » Post Date: 2024/4/25 , https://www.rokeecoupling.net/tags/geared-couplings.html