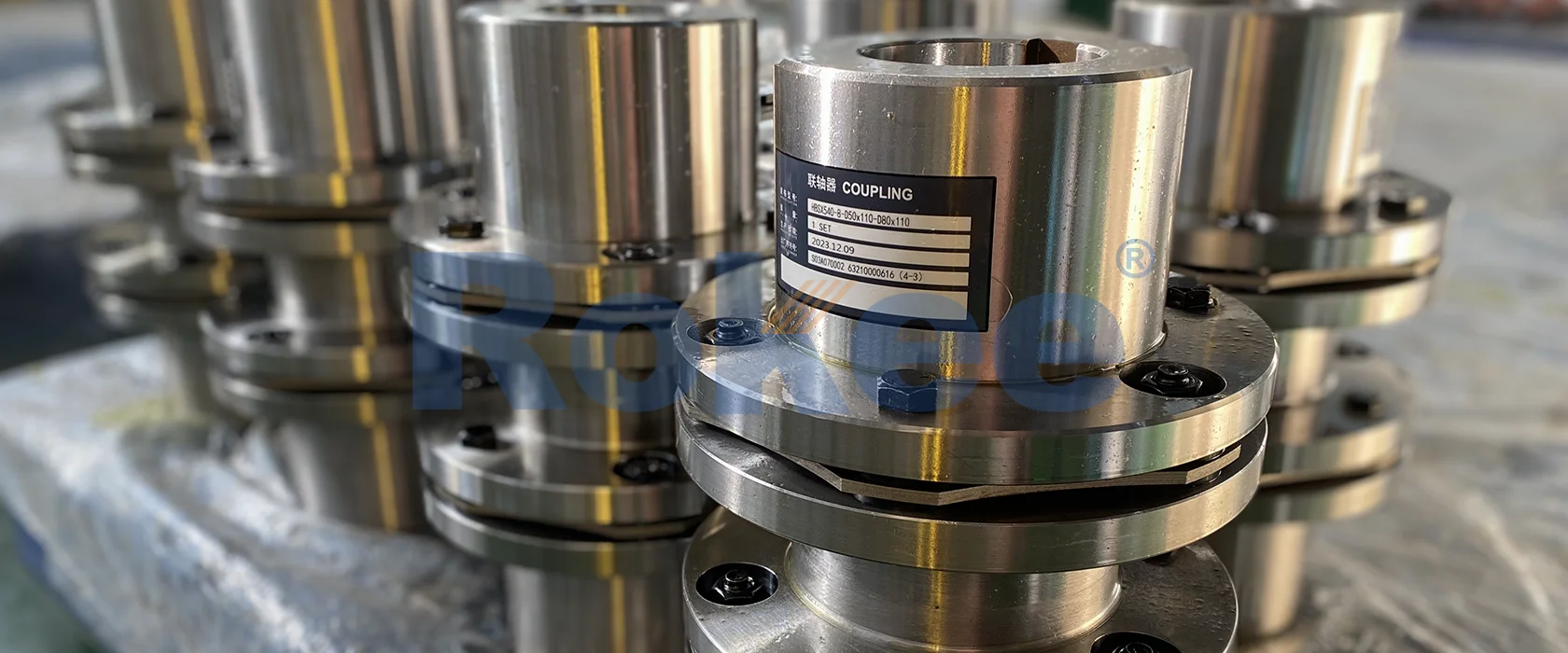

Rokee is a well-known high-quality supplier of Plate Couplings and technical services in China, customize plate couplings according to user drawings, alternatively, if the user provides plate couplings parameters, we can select the model and design drawings for you, support wholesale and export.




In the complex network of mechanical power transmission, couplings act as the vital link between rotating shafts, facilitating torque transfer while addressing inherent challenges such as misalignment, vibration, and shock loads. Among the diverse spectrum of coupling technologies, plate couplings have secured a prominent position in industrial and commercial applications due to their unique blend of rigidity, flexibility, and reliability. Unlike elastic couplings that rely on rubber or polymer elements, plate couplings utilize metal plates (typically metallic discs or diaphragms) to transmit torque, offering distinct advantages in high-speed, high-torque, and harsh-environment operations. This article provides an in-depth exploration of plate couplings, covering their fundamental design principles, operational mechanisms, material considerations, key applications across industries, installation and maintenance protocols, technological advancements, and inherent limitations.
At the core of a plate coupling’s functionality lies its innovative design, which enables efficient torque transmission while accommodating limited misalignment. A standard plate coupling consists of three primary components: two shaft hubs (or flanges) that attach to the driving and driven shafts, and a series of metal plates (the coupling’s flexible element) that connect these hubs. The metal plates are typically thin, flat, or slightly contoured, and are fastened to the hubs using bolts or studs. The number and configuration of the plates vary depending on the application’s torque requirements and misalignment tolerance—multiple plates are often stacked to enhance torque capacity and flexibility. When the driving shaft rotates, torque is transferred from the driving hub to the metal plates. The plates, due to their inherent flexibility, deform slightly to accommodate axial, radial, and angular misalignment between the two shafts, then transmit the rotational force to the driven hub and shaft. This deformation is elastic, meaning the plates return to their original shape once the load is removed, ensuring consistent performance over time.
A key distinction between plate couplings and other flexible coupling types is the nature of their flexibility. Unlike rubber tyre couplings that rely on the elastic deformation of polymer materials, plate couplings achieve flexibility through the bending and torsion of the metal plates. This metallic flexibility offers several advantages: superior resistance to high temperatures, chemicals, and wear; higher torque and speed capabilities; and minimal hysteretic loss (energy loss due to material deformation). Additionally, plate couplings do not require lubrication, eliminating the risk of lubricant leakage and reducing maintenance requirements—a critical benefit in applications where contamination is a concern, such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, or clean energy systems.
The structural design of plate couplings can be categorized into two main types: single-plate and multi-plate configurations. Single-plate couplings use a single thick or reinforced metal plate to connect the hubs, offering simplicity and cost-effectiveness for low to moderate torque applications. Multi-plate couplings, by contrast, employ a stack of thinner plates separated by spacers. This design distributes the load across multiple plates, increasing torque capacity and enhancing flexibility. The plates themselves can be designed with various geometries, such as circular, square, or with cutouts (e.g., bellows or slotted designs) to optimize flexibility and reduce stress concentrations. The hubs are typically manufactured from high-strength materials such as steel, stainless steel, or aluminum alloy, depending on the application’s requirements for strength, weight, and corrosion resistance. The connection between the plates and hubs is critical—bolted connections are the most common, with precision-machined holes ensuring accurate alignment and secure fastening.
Material selection is a decisive factor in determining the performance, durability, and application range of plate couplings. The metal plates, being the primary torque-transmitting and flexible elements, are typically made from high-performance alloys that combine strength, flexibility, and resistance to fatigue. The most commonly used materials for plates include stainless steel (e.g., 304, 316), carbon steel, and titanium alloy. Stainless steel is preferred for most industrial applications due to its excellent corrosion resistance, high tensile strength, and ability to withstand moderate to high temperatures (up to 500°C for some grades). Carbon steel offers superior strength and torque capacity but is more susceptible to corrosion, making it suitable for indoor, dry environments or applications where corrosion protection (e.g., painting, galvanizing) is applied. Titanium alloy, though more expensive, provides exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to extreme temperatures and harsh chemicals, making it ideal for specialized applications such as aerospace, marine, and high-performance industrial machinery.
The hubs, which must withstand the torque transmitted from the shafts to the plates, are typically fabricated from carbon steel or alloy steel for high-torque applications, or aluminum alloy for lightweight, low-torque applications. Stainless steel hubs are used in corrosive environments, such as marine or chemical processing facilities. In addition to the base materials, surface treatments may be applied to enhance performance—for example, galvanizing or chrome plating to improve corrosion resistance, or heat treatment to increase the hardness and strength of the hubs and plates.
The unique combination of properties offered by plate couplings makes them suitable for a wide range of applications across diverse industries. One of the primary application areas is in industrial machinery, where they are used to connect motors, pumps, compressors, fans, and gearboxes. In pump systems, for instance, plate couplings provide reliable torque transmission while accommodating the slight misalignments that occur due to thermal expansion or installation tolerances, reducing wear on the pump’s bearings and seals. In compressor systems, their high-speed capability and lack of lubrication make them ideal for preventing contamination of the compressed air or gas. Plate couplings are also widely used in the power generation industry, where they connect turbines to generators, handling high torque and high rotational speeds while accommodating the thermal expansion of the shafts.
The automotive and transportation industry is another major user of plate couplings, particularly in heavy-duty vehicles such as trucks, buses, and construction equipment. They are used in the transmission systems to connect the engine to the gearbox, providing robust torque transmission and absorbing the shock loads generated during acceleration and deceleration. In electric vehicles (EVs), plate couplings are increasingly being used due to their lightweight design and high efficiency, which contribute to improving the vehicle’s range. The aerospace industry employs plate couplings in aircraft engines and auxiliary power units (APUs), where their high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to extreme temperatures are critical for reliable operation in the harsh conditions of flight.
The food processing and pharmaceutical industries also benefit from plate couplings, as their lubrication-free design prevents contamination of the products. In these applications, stainless steel plate couplings are preferred due to their ease of cleaning and resistance to corrosion from the cleaning chemicals used. Additionally, plate couplings are used in marine applications, such as connecting the engine to the propeller shaft of ships and boats, where their corrosion resistance to saltwater and ability to accommodate misalignments caused by the vessel’s movement are essential.
Proper installation is critical to ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of plate couplings. The first step in installation is the accurate alignment of the driving and driven shafts. While plate couplings can accommodate limited misalignment (typically up to 0.5 degrees angular misalignment and 0.2 mm radial misalignment, depending on the design), excessive misalignment will cause increased stress on the plates, leading to premature fatigue failure. Precision alignment tools, such as laser alignment systems or dial indicators, should be used to ensure that the shafts are aligned within the manufacturer’s recommended tolerances. It is important to check both static alignment (when the machinery is not running) and dynamic alignment (when the machinery is operating at full speed), as thermal expansion can cause changes in alignment during operation.
The next step is the installation of the hubs onto the shafts. This typically involves using keyways and set screws, or interference fits (press fits), to ensure a secure connection between the hub and the shaft. The hubs must be positioned correctly to ensure that the plates are not under tension or compression when the coupling is assembled. Once the hubs are installed, the metal plates are attached using the specified bolts or studs. It is crucial to torque the bolts to the manufacturer’s recommended values—under-tightening can lead to loose connections and vibration, while over-tightening can cause deformation of the plates or hubs, reducing flexibility and increasing stress. After assembly, a final inspection should be performed to ensure that all components are properly seated, there is no interference between the coupling and other machinery parts, and the shafts rotate freely without binding.
Regular maintenance is essential to prevent unexpected failures and extend the service life of plate couplings. Unlike lubricated couplings, plate couplings require minimal maintenance, but periodic inspections are still necessary. The primary maintenance task is the regular inspection of the metal plates for signs of fatigue, wear, or damage. This includes checking for cracks, bending, or deformation of the plates, which can indicate that the coupling is operating beyond its design limits or that misalignment has occurred. The bolts and fasteners should also be inspected regularly to ensure that they are tight and not damaged—loose bolts can cause excessive vibration and misalignment, leading to premature failure of the plates.
In corrosive environments, additional maintenance steps may be required, such as cleaning the coupling components to remove salt, dust, or chemical residues, and inspecting for signs of corrosion. If corrosion is detected, the affected components should be replaced or treated to prevent further damage. It is also important to monitor the operating temperature of the coupling, as excessive heat can indicate misalignment, overloading, or material degradation. In applications where the coupling is exposed to high temperatures or harsh chemicals, regular replacement of the plates may be necessary to ensure reliable performance.
Technological advancements in recent years have led to significant improvements in the design and performance of plate couplings. One of the key areas of innovation is the development of advanced material alloys for the plates and hubs. For example, the use of composite materials (such as carbon fiber-reinforced polymers) in combination with metals has resulted in couplings that are lighter, stronger, and more resistant to fatigue than traditional all-metal designs. These composite plate couplings are particularly suitable for applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in aerospace and electric vehicles.
Another area of advancement is the integration of smart monitoring technologies into plate couplings. Modern couplings are increasingly equipped with sensors that measure parameters such as temperature, vibration, and torque. This real-time data is transmitted to a central monitoring system, allowing maintenance personnel to detect early signs of wear, misalignment, or overloading. Predictive maintenance based on this data helps to reduce downtime, lower maintenance costs, and improve the overall reliability of the machinery. Additionally, advancements in manufacturing processes, such as precision machining and 3D printing, have enabled the production of plate couplings with complex geometries that optimize flexibility and torque capacity while reducing weight and material waste.
Despite their numerous advantages, plate couplings also have certain limitations that must be considered when selecting a coupling for a specific application. One of the main limitations is their limited misalignment tolerance compared to elastic couplings such as rubber tyre couplings. Plate couplings are designed to accommodate small to moderate misalignments, and excessive misalignment can lead to rapid fatigue failure of the plates. Another limitation is their higher cost compared to some other coupling types, particularly for specialized designs using high-performance materials such as titanium or composites. Additionally, plate couplings are not suitable for applications where significant shock absorption is required, as the metal plates have limited damping capabilities compared to rubber or polymer elements. In such applications, a combination of a plate coupling with a shock absorber may be necessary.
In conclusion, plate couplings are versatile and reliable components in mechanical power transmission systems, offering a unique combination of rigidity, flexibility, high torque capacity, and low maintenance requirements. Their design, which utilizes metal plates for torque transmission and misalignment accommodation, makes them particularly suitable for high-speed, high-torque, and harsh-environment applications across industries such as industrial machinery, power generation, automotive, aerospace, and food processing. Material selection plays a crucial role in their performance, with stainless steel, carbon steel, and titanium alloy being the most commonly used materials for plates and hubs. Proper installation and regular maintenance are essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity, while recent technological advancements in materials and monitoring systems have further enhanced their capabilities.
Despite their limitations, plate couplings continue to be a preferred choice for many critical applications due to their durability, efficiency, and contamination-free operation. As industries continue to evolve and demand higher performance, lighter weight, and more reliable transmission systems, plate couplings are likely to undergo further innovations, solidifying their position as a key component in modern mechanical systems. Whether in a large power plant, a heavy-duty truck, or a precision pharmaceutical machine, plate couplings play an indispensable role in ensuring the smooth and efficient transfer of power, contributing to the overall productivity and reliability of industrial operations.
« Plate Couplings » Post Date: 2024/4/25 , https://www.rokeecoupling.net/tags/plate-couplings.html