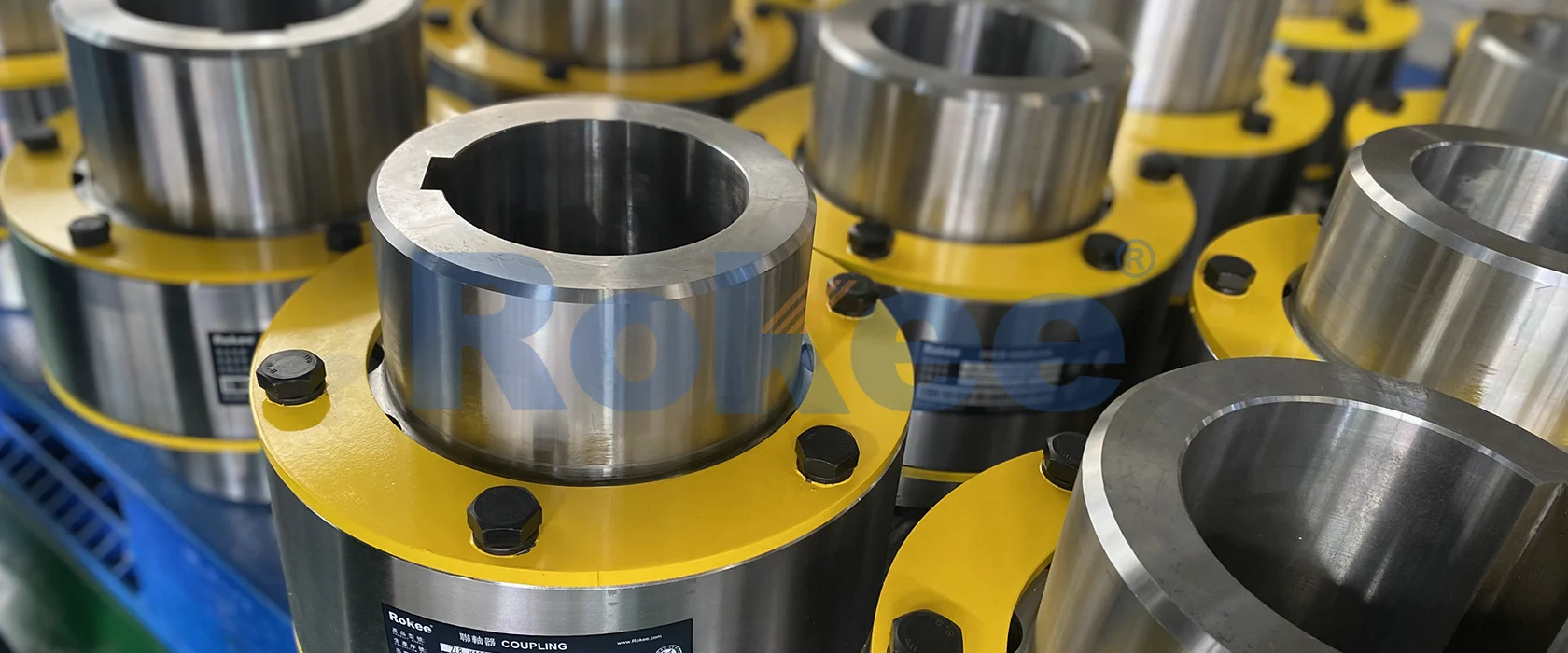

Rokee is a well-known high-quality supplier of Crown Pin Couplings and technical services in China, customize crown pin couplings according to user drawings, alternatively, if the user provides crown pin couplings parameters, we can select the model and design drawings for you, support wholesale and export.
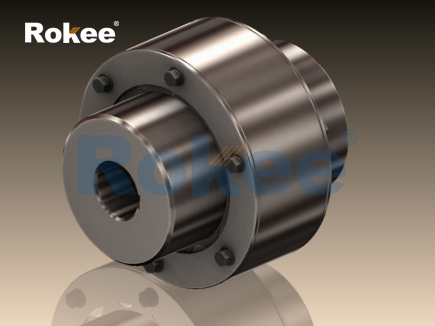



Crown pin coupling is an advanced mechanical transmission connection device that has been widely used in the industrial transmission field in recent years. This type of coupling achieves high torque transmission and excellent eccentricity compensation capability through a unique crown tooth structure and precise pin shaft coordination.
Coronal toothed flange: made of alloy steel with special heat treatment process, with a tooth design as a coronal curved surface
Elastic pin component: a cushioning element made of high-strength engineering plastic or special rubber material
Positioning pin system: Precision machined pin shafts ensure accurate alignment of connections
During operation, torque is transmitted through the crown tooth surface to the elastic pin, and then transmitted from the pin to the other flange. Elastic components can effectively absorb impact vibrations, while the coronal surface design allows for certain angular and radial deviations.
High torque density: The unique tooth design increases torque transmission per unit volume by 30-40% compared to traditional couplings
Excellent deviation compensation:
The angular deviation compensation capability can reach ± 3 °
Radial deviation compensation up to 0.5mm
Axial floating distance ± 2mm
Maintenance free design: adopting long-term lubrication technology, with a typical service life of 50000 hours
Vibration and noise reduction: Elastic components can reduce transmission system noise by 15-20 decibels
Quick installation: No special tools required, installation time saves 60% compared to traditional couplings
High precision machine tools: spindle drive for CNC lathes and machining centers
Wind power equipment: connection between generator and gearbox
Ship propulsion system: elastic connection between main engine and shaft system
Iron and Steel Metallurgy: Heavy Load Application of Rolling Mill Transmission System
Automated production line: robot joint transmission
Torque demand: including rated torque and peak torque
Speed range: The maximum working speed does not exceed 80% of the coupling's maximum speed
Environmental conditions: temperature, humidity, corrosive media, etc
Deviation requirement: Select the appropriate model based on the actual deviation of the equipment
Space limitations: radial and axial dimensions of installation space
Crown pin couplings with their excellent performance and reliability, are gradually replacing traditional couplings and becoming the preferred solution for modern industrial transmission systems. With the advancement of manufacturing technology, its application fields will further expand.
In the complex ecosystem of mechanical power transmission, couplings serve as the critical link between rotating shafts, ensuring seamless torque transfer while accommodating misalignments and mitigating operational stresses. Among the diverse range of coupling designs, the crown pin coupling stands out as a versatile and robust solution, widely adopted across industrial sectors for its balanced combination of simplicity, durability, and performance. This mechanical component plays an indispensable role in bridging the gap between prime movers and driven machinery, adapting to varying operating conditions while minimizing energy loss and equipment wear. To fully appreciate the value of crown pin couplings in modern industrial applications, it is essential to explore their structural composition, operational principles, material selection, design considerations, installation procedures, maintenance practices, application scenarios, and comparative advantages relative to other coupling types.
At its core, the crown pin coupling is a flexible coupling variant characterized by a modular design that facilitates torque transmission through non-metallic flexible elements. Unlike rigid couplings that demand precise alignment and offer no flexibility, crown pin couplings leverage the deformability of specialized components to absorb shocks, dampen vibrations, and compensate for axial, radial, and angular misalignments between connected shafts. The fundamental structure of a crown pin coupling typically comprises two toothed semi-couplings, a toothed sleeve ring with an outer ring, and non-metallic flexible pins. Each semi-coupling is designed to attach to the respective shafts of the driving and driven equipment, featuring flange holes that align with the flexible pins. The toothed sleeve ring engages with the semi-couplings, creating a secure yet flexible connection that allows for relative movement without compromising torque transfer efficiency. The non-metallic pins, often constructed from rubber, urethane, or other elastomeric materials, serve as the primary flexible elements, deforming under load to accommodate misalignments and absorb impact forces generated during operation.
The operational principle of the crown pin coupling revolves around the synergy between its structural components, with each part contributing to the overall functionality and performance of the assembly. When the driving shaft rotates, torque is transmitted to the connected semi-coupling, which in turn exerts force on the non-metallic flexible pins. These pins deform slightly as they transfer the torque to the opposing semi-coupling, which then drives the driven shaft. This deformation of the flexible pins is key to the coupling’s ability to compensate for misalignments—whether caused by manufacturing tolerances, installation errors, thermal expansion, or operational deformation of equipment frames. Angular misalignment is addressed by the rotational flexibility of the pins, while radial and axial misalignments are accommodated through the elastic deformation of the non-metallic elements. Additionally, the flexible pins act as shock absorbers, dampening sudden load fluctuations and vibrations that would otherwise be transmitted to the connected machinery, thereby reducing wear on bearings, gears, and other critical components. The absence of lubrication requirements in most crown pin coupling designs further simplifies operation, as it eliminates the need for regular lubricant checks, refills, and the associated maintenance costs and downtime.
Material selection is a pivotal factor in determining the performance, durability, and suitability of crown pin couplings for specific operating conditions. The choice of materials for each component is guided by factors such as load capacity, operating speed, temperature range, environmental conditions (including exposure to moisture, chemicals, or abrasive particles), and desired service life. The semi-couplings and toothed sleeve ring, which bear the brunt of the torque and mechanical stress, are typically fabricated from high-strength metallic materials. Steel alloys are the most common choice for these components due to their excellent tensile strength, hardness, and wear resistance. Alloy steels, in particular, offer enhanced performance under high-load and high-temperature conditions, making them suitable for heavy-duty industrial applications. Some designs may utilize carbon steels for lighter-duty applications where cost-effectiveness is a priority, though these materials may have lower fatigue resistance and durability compared to alloy steels. In corrosive environments, materials such as stainless steel or metallic components with corrosion-resistant coatings (such as zinc plating or epoxy coatings) are often employed to prevent rust and degradation over time.
The non-metallic flexible pins, being the primary flexible and shock-absorbing elements, require materials with optimal elasticity, wear resistance, and resistance to environmental factors. Chloroprene rubber (neoprene) is a widely used material for these pins, offering excellent flexibility, good wear resistance, and resistance to oils, chemicals, and moderate temperatures. Urethane is another popular choice, known for its higher load-bearing capacity and abrasion resistance compared to rubber, making it suitable for applications with higher torque requirements or exposure to abrasive particles. For high-temperature applications, silicone-based elastomers may be utilized, as they maintain their flexibility and structural integrity at elevated temperatures that would cause rubber or urethane to degrade. The selection of the pin material must also consider the operating temperature range, as extreme cold can cause elastomers to become brittle, while excessive heat can lead to softening, deformation, and premature failure. In some specialized applications, composite materials may be used to enhance the mechanical properties of the pins, such as incorporating reinforcing fibers to improve tensile strength without compromising flexibility.
Design considerations for crown pin couplings are multifaceted, encompassing load capacity, misalignment compensation, operating speed, structural integrity, and ease of installation and maintenance. Load capacity is a primary design parameter, with couplings rated based on their ability to transmit torque under normal and peak operating conditions. The maximum torque capacity of a crown pin coupling is determined by the strength of the semi-couplings, the cross-sectional area of the flexible pins, and the material properties of both metallic and non-metallic components. Engineers must account for not only the nominal torque required for continuous operation but also the impact loads and torque spikes that may occur during start-up, shutdown, or sudden changes in operating conditions. Service factors are typically applied to the nominal torque to ensure the coupling can withstand these variable loads, with the service factor varying based on the type of prime mover (e.g., electric motor, internal combustion engine) and the nature of the driven load (e.g., steady, medium impulsive, highly impulsive). For example, applications with internal combustion engines, which produce more impulsive loads, require higher service factors than those driven by electric motors, which provide relatively steady torque.
Misalignment compensation capability is another critical design consideration, as even minor misalignments can lead to increased vibration, reduced efficiency, and premature component failure. Crown pin couplings are designed to accommodate specific ranges of axial, radial, and angular misalignment, with the exact values depending on the coupling size, pin material, and structural design. Angular misalignment compensation is particularly important in applications where shaft alignment is challenging, such as in large industrial machinery where thermal expansion or structural deformation can cause dynamic misalignments during operation. The toothed design of the semi-couplings and sleeve ring further enhances misalignment compensation by allowing for smooth relative movement between the components without excessive friction or wear. Operating speed is also a key factor, as higher rotational speeds can generate centrifugal forces that impact the stability of the coupling. Designers must ensure that the coupling components are balanced to minimize vibration at operating speeds, with careful attention to the weight distribution of the semi-couplings and the flexibility of the pins to avoid resonance.
Ease of installation and maintenance is integrated into the design of crown pin couplings to minimize downtime and operational costs. The modular design allows for straightforward assembly and disassembly, with the semi-couplings easily mounted on the shafts using keys or set screws. The flexible pins can be replaced without removing the entire coupling from the shafts, a feature that significantly reduces maintenance time compared to couplings with more complex designs. Some crown pin coupling variants include additional features to enhance usability, such as conical shaft holes to facilitate easier mounting on tapered shafts or brake wheels for applications requiring integrated braking functionality. The absence of lubrication requirements further simplifies maintenance, as it eliminates the need for specialized lubrication equipment and regular inspections to ensure proper lubricant levels and quality. However, designers must ensure that the coupling design allows for easy access to the flexible pins for inspection and replacement, as worn or damaged pins can compromise the coupling’s performance and lead to equipment failure.
Proper installation is essential to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of crown pin couplings. The installation process begins with thorough preparation, including verifying the availability of all components, ensuring the installation area is clean and free of obstacles, and checking that the necessary tools (such as torque wrenches, alignment tools, and lifting equipment) are in good working order. Installation personnel should also wear appropriate safety gear, including gloves, safety glasses, and steel-toed boots, to minimize the risk of injury during the process. The first step in installation is to mount the semi-couplings on the respective shafts of the driving and driven equipment. This involves cleaning the shaft surfaces to remove any dirt, rust, or debris that could affect the fit, then sliding the semi-couplings onto the shafts and securing them using keys and set screws or other fastening methods. It is critical to ensure that the semi-couplings are positioned correctly on the shafts, with sufficient clearance between the coupling components to accommodate axial movement and misalignment.
Shaft alignment is a critical step in the installation process, as improper alignment can lead to excessive vibration, premature wear of the flexible pins and other components, and reduced coupling efficiency. Alignment can be checked using simple tools such as straightedges or dial gauges, which measure the radial and angular deviations between the two semi-couplings. For more precise alignment, laser alignment tools may be used, particularly in high-speed or high-precision applications. The alignment process involves adjusting the position of the driven equipment (or, in some cases, the driving equipment) to minimize misalignment, with adjustments made to the base plates or mounting brackets as needed. Once the shafts are properly aligned, the flexible pins are inserted through the flange holes of the semi-couplings, and the toothed sleeve ring is positioned to engage with both semi-couplings. Care should be taken to ensure that the pins are fully seated and that the sleeve ring is properly aligned to avoid binding or excessive friction. Finally, all fasteners are tightened to the recommended torque specifications to ensure a secure connection.
Post-installation inspection is an important part of the process, involving a visual check of all components to ensure proper assembly and alignment. The coupling should be rotated manually to verify that there is no binding or excessive resistance, and the connected machinery should be run at low speed initially to check for vibration, noise, or abnormal heating. Any issues identified during this test run should be addressed immediately, as prolonged operation with misaligned or improperly assembled couplings can lead to severe damage to the coupling and connected equipment. Regular maintenance is also essential to maximize the service life of crown pin couplings. Maintenance activities typically include periodic inspections of the flexible pins for signs of wear, cracking, or deformation, as these are the most vulnerable components. Inspections should be conducted at regular intervals based on the operating conditions, with more frequent checks in harsh or high-load environments. Worn or damaged pins should be replaced promptly to prevent further damage to the semi-couplings or connected shafts.
In addition to pin inspection, maintenance should include checking the tightness of all fasteners, as vibration during operation can cause set screws and other fasteners to loosen over time. The semi-couplings and sleeve ring should be inspected for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage to the toothed surfaces, as worn teeth can reduce torque transmission efficiency and increase noise. If corrosion is detected, the affected components should be cleaned and treated with a corrosion-resistant coating to prevent further degradation. For couplings used in dusty or abrasive environments, periodic cleaning may be necessary to remove debris that could accumulate on the components and cause excessive wear. It is also important to monitor the operating temperature of the coupling, as abnormal heating can indicate issues such as misalignment, worn pins, or excessive load. By following a proactive maintenance schedule, operators can identify potential problems early and address them before they result in unplanned downtime or equipment failure.
Crown pin couplings find applications across a wide range of industrial sectors, thanks to their versatility, durability, and low maintenance requirements. One of the primary application areas is in lifting and transportation equipment, such as cranes, hoists, and conveyors. These applications often involve variable loads, frequent start-ups and shutdowns, and potential misalignments due to the dynamic nature of the equipment, making crown pin couplings an ideal choice. The shock absorption capability of the flexible pins helps to protect the crane’s motor, gearbox, and lifting mechanism from the impact forces generated during lifting and lowering operations, while the misalignment compensation ensures smooth operation even when the equipment is subjected to structural deformation. In addition, the absence of lubrication requirements is particularly beneficial in these applications, as it eliminates the risk of lubricant contamination in work environments where cleanliness is important.
Another major application area for crown pin couplings is in the metallurgical industry, where they are used in equipment such as rolling mills, blast furnaces, and conveyor systems. Metallurgical processes involve high temperatures, heavy loads, and harsh operating conditions, requiring couplings that can withstand extreme environments while maintaining reliable performance. The high-strength metallic components of crown pin couplings resist thermal expansion and deformation, while the flexible pins absorb the vibrations and shock loads generated by the rolling and processing of metal. The ability to accommodate misalignments is also critical in these applications, as the high temperatures can cause significant thermal expansion of the equipment frames and shafts, leading to dynamic misalignments during operation. Crown pin couplings are also used in the mining industry, where they connect motors, pumps, and conveyors in underground and surface mining operations. The rugged design of these couplings withstands the abrasive and dusty environments common in mining, while the shock absorption capability protects equipment from the heavy loads and impact forces associated with mining operations.
In the general machinery sector, crown pin couplings are widely used in pumps, compressors, fans, and generators. These applications often require reliable torque transmission with minimal maintenance, and the simplicity of crown pin couplings makes them a cost-effective solution. For example, in water and wastewater treatment plants, crown pin couplings connect electric motors to pumps, ensuring efficient water transfer while accommodating misalignments caused by the installation of the pump and motor on different base plates. The non-metallic pins resist corrosion from water and chemicals, ensuring long service life in these environments. In HVAC systems, crown pin couplings are used in fans and blowers, where their vibration dampening capability helps to reduce noise and improve the comfort of building occupants. The low maintenance requirements of these couplings are particularly beneficial in HVAC applications, as they reduce the need for regular servicing and minimize downtime.
Specialized applications of crown pin couplings include use in wave machines for Olympic pools and other recreational facilities. These applications require couplings that can transmit torque smoothly while accommodating the dynamic misalignments caused by the movement of the wave-generating equipment. The flexible pins absorb the vibrations and shock loads generated by the wave machine, ensuring quiet and reliable operation. Crown pin couplings are also used in renewable energy applications, such as small wind turbines and hydroelectric generators, where their durability and low maintenance requirements make them suitable for remote locations. In these applications, the ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures and moisture, is critical, and the corrosion-resistant materials used in many crown pin coupling designs ensure reliable performance over time.
To understand the unique value of crown pin couplings, it is helpful to compare them with other common coupling types, such as gear couplings, elastic sleeve pin couplings, and universal joints. Gear couplings are known for their high torque capacity and durability, but they require regular lubrication and have limited misalignment compensation capability compared to crown pin couplings. Gear couplings also tend to be more expensive and complex to maintain, making them less suitable for applications where low maintenance is a priority. Elastic sleeve pin couplings are similar to crown pin couplings in that they use non-metallic elements for flexibility, but they have lower torque capacity and misalignment compensation capability. Elastic sleeve pin couplings are typically used in lighter-duty applications, while crown pin couplings are better suited for medium to heavy-duty loads.
Universal joints are designed to accommodate large angular misalignments, but they are prone to generating vibration at high speeds and have lower torque capacity compared to crown pin couplings. Universal joints also require more maintenance, including lubrication and periodic inspection of the bearings, making them less ideal for continuous operation in harsh environments. Crown pin couplings strike a balance between torque capacity, misalignment compensation, and maintenance requirements, making them a versatile choice for a wide range of applications. Their ability to operate without lubrication, combined with their modular design and easy maintenance, gives them a distinct advantage over many other coupling types in terms of operational cost and downtime reduction.
Despite their many advantages, crown pin couplings have certain limitations that must be considered when selecting a coupling for a specific application. One of the primary limitations is their suitability for high-speed applications. While crown pin couplings can handle moderate to high speeds, excessive rotational speeds can cause the flexible pins to experience excessive centrifugal forces, leading to premature wear or failure. In applications with very high speeds, other coupling types, such as disc couplings, may be more appropriate. Another limitation is the temperature range of the non-metallic pins. Elastomeric pins can degrade at extreme temperatures, either becoming brittle in cold conditions or softening in hot conditions, which can reduce their flexibility and load-bearing capacity. For applications with extreme temperature ranges, specialized pin materials or alternative coupling designs may be necessary.
Crown pin couplings also have limited axial misalignment compensation compared to some other flexible coupling types, such as bellows couplings. This means they may not be suitable for applications where significant axial movement is expected, such as in equipment with large thermal expansion coefficients. Additionally, while crown pin couplings are resistant to moderate chemical exposure, they may not be suitable for applications with high concentrations of corrosive chemicals, as the non-metallic pins and metallic components can degrade over time. In such cases, corrosion-resistant materials or specialized couplings designed for chemical environments should be used.
The future of crown pin couplings is likely to be shaped by advancements in material science and manufacturing technology, leading to improved performance and expanded application ranges. Developments in elastomeric materials are expected to result in flexible pins with higher load-bearing capacity, better temperature resistance, and longer service life. For example, the use of nanocomposite elastomers, which incorporate nanoparticles to enhance mechanical properties, may lead to crown pin couplings that can withstand higher torques and extreme temperatures without compromising flexibility. Advancements in manufacturing processes, such as 3D printing, may also enable the production of customized crown pin couplings with complex geometries, allowing for optimized performance in specialized applications. 3D printing can also reduce lead times for custom couplings, making them more accessible for small-batch or specialized industrial applications.
Another trend in the development of crown pin couplings is the integration of smart technologies for condition monitoring. Sensors embedded in the coupling components can monitor parameters such as vibration, temperature, and pin wear, providing real-time data to operators. This allows for predictive maintenance, where potential issues are identified before they result in equipment failure, further reducing downtime and operational costs. Smart crown pin couplings may also be integrated into industrial internet of things (IIoT) systems, enabling remote monitoring and control of the coupling’s performance. This is particularly beneficial for applications in remote locations or large industrial facilities where regular on-site inspections are challenging.
In conclusion, crown pin couplings are a vital component in mechanical power transmission systems, offering a unique combination of simplicity, durability, flexibility, and low maintenance requirements. Their modular design, ability to compensate for misalignments, and shock absorption capability make them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications, from lifting equipment and metallurgical processes to pumps, fans, and renewable energy systems. Proper material selection, design, installation, and maintenance are essential to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of crown pin couplings, allowing them to withstand the demands of harsh operating conditions and variable loads. As material science and manufacturing technologies continue to advance, crown pin couplings are expected to become even more versatile and reliable, expanding their role in modern industrial systems and contributing to improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and lower operational costs. Whether in heavy-duty industrial applications or specialized systems, crown pin couplings remain a trusted and effective solution for connecting rotating shafts and transmitting torque with precision and reliability.
« Crown Pin Couplings » Latest Update Date: 2026/1/20 , https://www.rokeecoupling.net/tags/crown-pin-couplings.html