
Rokee is a well-known high-quality supplier of Flexible Diaphragm Couplings and technical services in China, customize flexible diaphragm couplings according to user drawings, alternatively, if the user provides flexible diaphragm couplings parameters, we can select the model and design drawings for you, support wholesale and export.




In the realm of mechanical power transmission, couplings serve as critical components that bridge rotating shafts, enabling the seamless transfer of torque while accommodating various forms of misalignment. Among the diverse range of couplings available, the flexible diaphragm coupling has emerged as a preferred choice in numerous industrial applications due to its unique combination of rigidity, flexibility, and reliability. Unlike traditional couplings that rely on rubber or elastomeric elements for flexibility, the flexible diaphragm coupling utilizes thin, precision-engineered metallic diaphragms to absorb misalignment and dampen minor vibrations. This design not only enhances the coupling’s durability under harsh operating conditions but also eliminates the need for lubrication, reducing maintenance requirements and operational costs. This article delves into the fundamental principles, structural characteristics, material selection, key advantages, typical applications, and maintenance practices of flexible diaphragm couplings, providing a comprehensive overview of their role in modern mechanical systems.
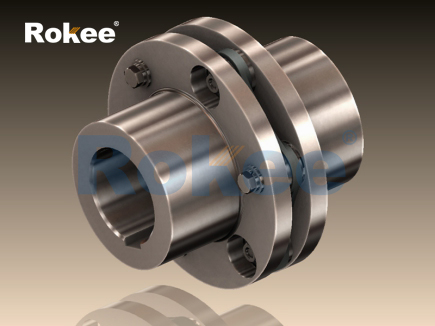
At its core, a flexible diaphragm coupling is designed to transmit torque from a driving shaft to a driven shaft while compensating for three primary types of misalignment: angular misalignment (where the shafts are inclined relative to each other), parallel misalignment (where the shafts are offset radially), and axial misalignment (where the shafts move toward or away from each other). The key to achieving this lies in the flexible diaphragms, which act as the coupling’s "flexible element." These diaphragms are typically arranged in one or more sets, connected between the coupling’s hubs and a central spacer (in the case of long-coupled designs) or directly between the two hubs (in short-coupled designs).
When torque is applied, the diaphragms undergo elastic deformation to accommodate misalignment without compromising the transmission of power. The metallic diaphragms are engineered to handle both tensile and compressive forces, ensuring that torque is transferred efficiently even as the coupling adjusts to shaft misalignment. Unlike couplings with sliding or rolling components, the flexible diaphragm coupling operates with zero backlash, meaning there is no play or lost motion between the driving and driven shafts. This zero-backlash characteristic is particularly crucial in applications requiring precise positioning and synchronization, such as in robotics, machine tools, and precision manufacturing equipment.
Another fundamental principle of the flexible diaphragm coupling is its ability to operate without lubrication. Since the diaphragms transmit torque through elastic deformation rather than through frictional contact, there is no need for grease or oil to reduce wear. This not only simplifies maintenance but also eliminates the risk of lubricant contamination, making the coupling suitable for applications in clean environments, such as food processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and semiconductor production.
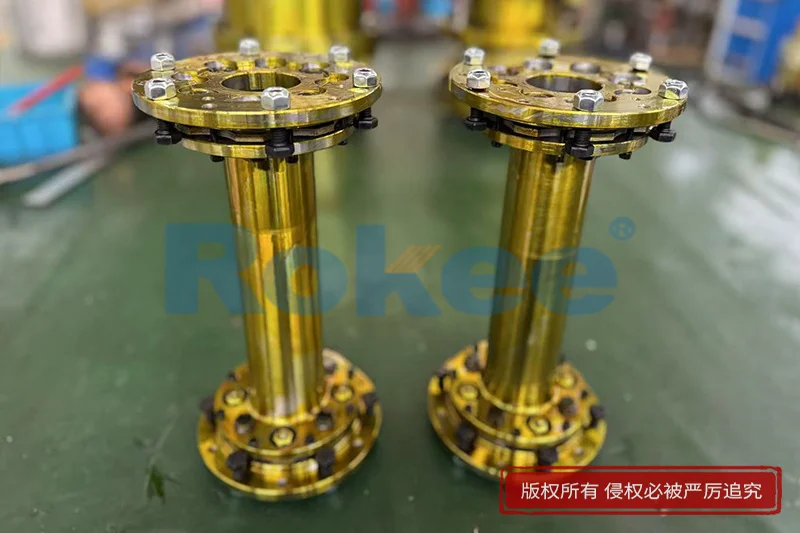
Flexible diaphragm couplings exhibit a relatively simple yet robust structure, consisting of several key components: hubs, diaphragms, a spacer (optional), and fasteners. Each component is designed to work in harmony to ensure efficient torque transmission and misalignment compensation.
The hubs are the connecting elements that attach the coupling to the driving and driven shafts. They are typically manufactured from high-strength metals such as steel or aluminum alloy, depending on the application’s torque requirements and weight constraints. Hubs are often designed with keyways, splines, or compression fittings to ensure a secure, slip-free connection to the shafts. In some cases, hydraulic or interference fits may be used for high-torque applications where maximum reliability is essential.
The diaphragms are the most critical component of the coupling, responsible for providing flexibility and torque transmission. They are thin, disc-shaped or bellows-shaped elements made from metallic materials (discussed in detail in the next section). Diaphragms are usually attached to the hubs and spacer (if present) using high-strength bolts or rivets. The number and thickness of the diaphragms vary depending on the coupling’s torque capacity and the amount of misalignment it needs to accommodate. Multiple diaphragms are often used in parallel to increase the coupling’s torque rating and enhance its ability to absorb misalignment.
Spacers are optional components used in long-coupled designs to separate the two hubs, allowing for greater axial misalignment and facilitating easier installation and maintenance. Spacers can be solid or hollow, and their length can be customized to meet the specific requirements of the application. In some cases, spacers are designed to be replaceable, enabling quick adjustments or repairs without disassembling the entire coupling.
Fasteners, such as bolts, nuts, and washers, are used to secure the diaphragms to the hubs and spacer. These fasteners are typically made from high-strength alloys to ensure they can withstand the tensile and compressive forces generated during operation. Proper torquing of the fasteners is critical to maintaining the coupling’s integrity, as loose fasteners can lead to vibration, noise, and premature failure.
There are two main types of flexible diaphragm coupling designs: single-diaphragm and double-diaphragm. Single-diaphragm couplings have a single set of diaphragms, making them compact and lightweight. They are suitable for applications with moderate misalignment requirements. Double-diaphragm couplings, on the other hand, have two sets of diaphragms, one on each end of the spacer. This design provides greater misalignment compensation, particularly for angular and axial misalignment, and helps to reduce the bending moments transmitted to the shafts. Double-diaphragm couplings are often used in high-precision and high-torque applications where shaft protection is a priority.
The performance and durability of a flexible diaphragm coupling are heavily dependent on the materials used for its components, particularly the diaphragms. The selection of materials is influenced by a range of factors, including the application’s operating temperature, torque requirements, environmental conditions (such as corrosion or exposure to chemicals), and weight constraints.
For diaphragms, the most commonly used materials are high-strength metallic alloys, which offer excellent elastic properties, fatigue resistance, and thermal stability. Stainless steel is a popular choice for many applications due to its corrosion resistance and high strength-to-weight ratio. Austenitic stainless steels, such as 304 and 316, are widely used in food processing, pharmaceutical, and marine applications where corrosion resistance is critical. For high-temperature applications, such as in gas turbines or industrial furnaces, nickel-based alloys (such as Inconel or Hastelloy) are preferred due to their ability to maintain their mechanical properties at temperatures exceeding 500°C.
In applications where weight is a major concern, such as in aerospace or automotive systems, aluminum alloys may be used for the diaphragms and hubs. However, aluminum alloys have lower fatigue resistance and temperature tolerance compared to stainless steel or nickel-based alloys, so they are typically limited to low-torque, low-temperature applications.
The hubs and spacers are usually made from carbon steel, alloy steel, or aluminum alloy. Carbon steel is a cost-effective option for low to moderate torque applications, while alloy steel (such as 4140 or 4340) is used for high-torque applications due to its higher strength and toughness. Aluminum alloy hubs and spacers are used in lightweight applications, such as in robotics or small electric motors, where reducing the overall weight of the system is essential.
Fasteners are typically made from high-strength steel or stainless steel, depending on the environmental conditions. In corrosive environments, stainless steel fasteners are used to prevent rust and degradation. For high-torque applications, alloy steel fasteners with high tensile strength are preferred to ensure they can withstand the forces generated during operation.
Flexible diaphragm couplings offer a range of advantages over other types of couplings, making them suitable for a wide variety of industrial applications. These advantages include high torque capacity, zero backlash, no lubrication requirements, excellent misalignment compensation, compact design, and long service life.
One of the primary advantages of flexible diaphragm couplings is their high torque capacity. The metallic diaphragms are capable of transmitting large amounts of torque without slipping or deforming permanently, making them suitable for high-power applications such as industrial motors, pumps, compressors, and turbines. Unlike elastomeric couplings, which can degrade under high torque and temperature, flexible diaphragm couplings maintain their torque-carrying capacity even in harsh operating conditions.
Zero backlash is another key advantage of flexible diaphragm couplings. Backlash, or the amount of play between the driving and driven shafts, can cause inaccuracies in positioning and synchronization, particularly in precision applications. Since flexible diaphragm couplings transmit torque through elastic deformation of the diaphragms, there is no mechanical play, ensuring precise and reliable torque transmission. This makes them ideal for use in robotics, CNC machine tools, and other applications where positional accuracy is critical.
The elimination of lubrication requirements is a significant benefit in terms of maintenance and cost savings. Unlike gear couplings or universal joints, which require regular lubrication to prevent wear and corrosion, flexible diaphragm couplings operate without any lubricants. This not only reduces maintenance time and costs but also eliminates the risk of lubricant leakage and contamination, making them suitable for clean environments and applications where product purity is essential, such as in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
Flexible diaphragm couplings also offer excellent misalignment compensation capabilities. They can accommodate angular misalignment of up to 3 degrees (depending on the design), parallel misalignment of up to several millimeters, and axial misalignment of up to several centimeters. This ability to compensate for misalignment helps to reduce stress on the shafts, bearings, and other components of the mechanical system, extending their service life and reducing the risk of premature failure.
The compact and lightweight design of flexible diaphragm couplings makes them easy to install and integrate into existing mechanical systems. Unlike bulky gear couplings or universal joints, flexible diaphragm couplings have a small footprint, making them suitable for applications where space is limited. Their lightweight construction also helps to reduce the overall weight of the system, which is particularly important in aerospace, automotive, and robotics applications.
Finally, flexible diaphragm couplings have a long service life due to their robust design and the use of high-quality materials. The metallic diaphragms are resistant to fatigue, wear, and corrosion, and they do not degrade over time like elastomeric elements. With proper maintenance (discussed in the next section), flexible diaphragm couplings can operate reliably for many years, reducing downtime and replacement costs.
Due to their unique combination of advantages, flexible diaphragm couplings are used in a wide range of industrial, commercial, and aerospace applications. They are particularly well-suited for applications requiring high precision, high torque, clean operation, or resistance to harsh operating conditions.
In the aerospace industry, flexible diaphragm couplings are used in aircraft engines, auxiliary power units (APUs), and flight control systems. The lightweight and compact design of these couplings makes them ideal for use in aircraft, where weight and space are critical constraints. Their zero-backlash characteristic ensures precise torque transmission, which is essential for the reliable operation of flight control systems. Additionally, their resistance to high temperatures and corrosion makes them suitable for use in the harsh environment of aircraft engines.
In the automotive industry, flexible diaphragm couplings are used in electric vehicles (EVs), hybrid vehicles, and high-performance internal combustion engines. In EVs and hybrid vehicles, they are used to connect the electric motor to the transmission, providing efficient torque transmission and compensating for misalignment between the motor and transmission shafts. Their zero-backlash characteristic helps to improve the responsiveness of the vehicle’s drivetrain, while their lightweight design helps to reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, improving energy efficiency.
In the industrial sector, flexible diaphragm couplings are used in a wide range of equipment, including pumps, compressors, turbines, generators, and machine tools. In pump and compressor applications, they help to compensate for misalignment between the motor and pump/compressor shafts, reducing stress on the bearings and extending the service life of the equipment. In machine tools, such as CNC lathes and milling machines, their zero-backlash characteristic ensures precise positioning and machining accuracy, which is essential for producing high-quality components.
In the food and pharmaceutical industries, flexible diaphragm couplings are preferred due to their clean operation and lack of lubrication. They are used in processing equipment such as mixers, conveyors, and packaging machines, where product contamination must be avoided. Their corrosion-resistant materials (such as stainless steel) make them suitable for use in wet or corrosive environments, such as in food washing and sanitizing processes.
In the renewable energy sector, flexible diaphragm couplings are used in wind turbines and solar tracking systems. In wind turbines, they are used to connect the gearbox to the generator, transmitting the high torque generated by the turbine blades to the generator while compensating for misalignment between the gearbox and generator shafts. Their robust design and resistance to harsh weather conditions (such as wind, rain, and temperature fluctuations) make them suitable for use in offshore and onshore wind farms.
While flexible diaphragm couplings require less maintenance than many other types of couplings, proper maintenance is still essential to ensure their reliable operation and extend their service life. The key maintenance practices for flexible diaphragm couplings include regular inspection, proper installation, torque checking, and replacement of worn components.
Regular inspection is the most important maintenance practice for flexible diaphragm couplings. Inspections should be conducted periodically (depending on the application and operating conditions) to check for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. During inspection, the diaphragms should be checked for cracks, fatigue, or deformation. The hubs, spacer, and fasteners should also be inspected for signs of corrosion, wear, or loosening. Any signs of damage or wear should be addressed immediately to prevent premature failure of the coupling.
Proper installation is critical to the performance and service life of flexible diaphragm couplings. During installation, the shafts should be aligned as accurately as possible to minimize the amount of misalignment the coupling needs to accommodate. Misalignment beyond the coupling’s rated capacity can lead to excessive stress on the diaphragms, resulting in premature failure. The hubs should be properly secured to the shafts using the correct keyway, spline, or compression fitting, and the fasteners should be torqued to the manufacturer’s specifications.
Torque checking of the fasteners should be conducted regularly to ensure they remain tight. Loose fasteners can lead to vibration, noise, and misalignment, which can damage the coupling and other components of the mechanical system. The fasteners should be torqued to the manufacturer’s recommended values using a torque wrench, and any loose fasteners should be tightened immediately.
Replacement of worn components is necessary when signs of damage or wear are detected. The diaphragms are the most commonly replaced component, as they are subject to fatigue and deformation over time. When replacing diaphragms, it is important to use components that are compatible with the coupling’s design and specifications. The hubs, spacer, and fasteners should also be replaced if they show signs of excessive wear or corrosion.
In addition to these maintenance practices, it is important to operate the coupling within its rated parameters. Operating the coupling beyond its maximum torque capacity, misalignment limit, or temperature range can lead to premature failure. The manufacturer’s specifications should be followed closely to ensure the coupling is used correctly.
Flexible diaphragm couplings have established themselves as a reliable and efficient solution for torque transmission in a wide range of applications. Their unique design, which utilizes metallic diaphragms for flexibility and torque transmission, offers a range of advantages over other types of couplings, including high torque capacity, zero backlash, no lubrication requirements, excellent misalignment compensation, compact design, and long service life. The selection of materials for the coupling’s components, particularly the diaphragms, is critical to ensuring its performance and durability under various operating conditions.
From aerospace and automotive applications to industrial machinery and renewable energy systems, flexible diaphragm couplings play a vital role in ensuring the reliable and efficient operation of mechanical systems. Proper maintenance, including regular inspection, proper installation, torque checking, and replacement of worn components, is essential to maximizing the coupling’s service life and minimizing downtime.
As technology continues to advance, the design and performance of flexible diaphragm couplings are likely to be further optimized, making them even more suitable for emerging applications such as electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and advanced manufacturing equipment. With their unique combination of advantages, flexible diaphragm couplings are poised to remain a key component in mechanical power transmission for years to come.
« Flexible Diaphragm Couplings » Post Date: 2024/5/13 , https://www.rokeecoupling.net/tags/flexible-diaphragm-couplings.html