
Rokee is a well-known high-quality supplier of Single Diaphragm Couplings and technical services in China, customize single diaphragm couplings according to user drawings, alternatively, if the user provides single diaphragm couplings parameters, we can select the model and design drawings for you, support wholesale and export.


In the field of mechanical transmission, couplings play a pivotal role as critical components that connect two shafts (such as the output shaft of a motor and the input shaft of a working machine) to transmit torque and rotational motion. Among the diverse types of couplings available, the single diaphragm coupling has gained widespread recognition and application due to its unique structural design, excellent performance characteristics, and adaptability to various working conditions. Unlike rigid couplings that require precise alignment and lack flexibility, or elastic couplings that may suffer from fatigue failure of elastic elements, the single diaphragm coupling achieves torque transmission and compensation for shaft misalignment through the deformation of a single diaphragm. This article aims to comprehensively explore the single diaphragm coupling, including its structural composition, working principle, key advantages, typical application scenarios, selection criteria, and maintenance methods, providing a systematic understanding for engineering technicians and relevant professionals.
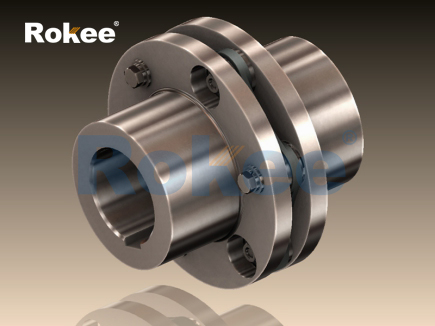
The structural design of the single diaphragm coupling is relatively concise yet ingenious, consisting of three main components: two shaft hubs, a single diaphragm, and connecting fasteners (such as bolts and nuts). The shaft hubs are usually made of high-strength alloy steel or carbon steel, which have good mechanical properties and wear resistance. Their inner holes are processed with keyways or adopt interference fit to ensure a tight connection with the driving and driven shafts, preventing relative sliding during torque transmission. The shape of the shaft hub can be customized according to the actual installation requirements, such as cylindrical, conical, or flanged structures. The single diaphragm is the core component of the coupling, which is a thin-walled circular or disc-shaped part made of high-quality elastic materials, typically stainless steel (such as 304, 316) or titanium alloy. These materials have excellent elastic deformation ability, fatigue resistance, and corrosion resistance, enabling the diaphragm to withstand repeated deformation during operation without permanent damage. The diaphragm is usually processed with multiple evenly distributed bolt holes around its circumference, which are used to connect with the two shaft hubs through fasteners. The design of the bolt holes and the distribution of the diaphragm's thickness are optimized through mechanical simulation and testing to ensure that the diaphragm can transmit torque efficiently while having sufficient flexibility to compensate for shaft misalignment.
The working principle of the single diaphragm coupling is based on the elastic deformation of the diaphragm. When the driving shaft rotates, it drives the driving shaft hub to rotate, and the torque is transmitted to the diaphragm through the connecting fasteners. The diaphragm, under the action of torque, generates elastic deformation, and then transmits the torque to the driven shaft hub, thereby driving the driven shaft to rotate. During this process, the single diaphragm can compensate for three types of shaft misalignment: axial displacement, radial displacement, and angular displacement. Axial displacement refers to the relative movement of the two shafts along the axial direction, which may be caused by thermal expansion and contraction of the shafts during operation or installation errors. The diaphragm's axial flexibility allows it to absorb this displacement without generating additional axial forces. Radial displacement is the offset of the two shafts in the radial direction, which may result from the deflection of the shafts due to load or the deformation of the equipment base. The radial deformation of the diaphragm can compensate for this offset, ensuring stable torque transmission. Angular displacement is the angle formed between the axes of the two shafts, which is often caused by improper installation or the inclination of the equipment. The diaphragm can generate bending deformation to adapt to this angular misalignment, avoiding the occurrence of additional bending moments on the shafts and bearings.
Compared with other types of couplings, the single diaphragm coupling has numerous distinct advantages that make it stand out in many applications. Firstly, it has high torque transmission efficiency. Due to the rigid connection between the diaphragm and the shaft hubs, there is almost no relative sliding during torque transmission, and the torque loss is minimal. The transmission efficiency can reach more than 99.5%, which is particularly important for equipment that requires high energy efficiency, such as electric motors and pumps. Secondly, it has excellent misalignment compensation capability. As mentioned earlier, the single diaphragm can effectively compensate for axial, radial, and angular misalignments, reducing the requirements for precise alignment during installation and reducing the wear and tear of shafts and bearings caused by misalignment. This not only simplifies the installation process but also extends the service life of the entire transmission system. Thirdly, it has no need for lubrication. Unlike gear couplings or universal joints that require regular lubrication to reduce friction and wear, the single diaphragm coupling has no sliding or rolling friction pairs. The only relative movement is the elastic deformation of the diaphragm, so it does not require lubricating oil or grease. This avoids the problems of lubricant leakage, pollution, and the need for regular lubrication maintenance, reducing the maintenance cost and workload. Fourthly, it has a compact structure and light weight. The simple structural composition makes the single diaphragm coupling smaller in size and lighter in weight compared to other couplings with similar torque transmission capacity. This is beneficial for reducing the overall weight and volume of the equipment, especially suitable for applications with limited installation space, such as aerospace, automotive, and precision machinery. Fifthly, it has good vibration damping performance. The elastic deformation of the diaphragm can absorb part of the vibration generated during the operation of the equipment, reducing the vibration transmission between the driving and driven shafts. This helps to reduce the noise of the equipment and improve the stability of the working process. Finally, it has strong environmental adaptability. The diaphragm made of stainless steel or titanium alloy has excellent corrosion resistance, high-temperature resistance, and low-temperature resistance, enabling the single diaphragm coupling to work normally in harsh environments such as humidity, corrosion, high temperature, and low temperature, which expands its application range.
Due to its excellent performance characteristics, the single diaphragm coupling is widely used in various fields of mechanical engineering. One of the typical application fields is the industrial pump industry. Pumps (such as centrifugal pumps, reciprocating pumps, and gear pumps) are widely used in water supply, drainage, chemical, petroleum, and other industries. The single diaphragm coupling is used to connect the motor and the pump shaft. Its high transmission efficiency ensures the energy-saving operation of the pump, and its misalignment compensation capability can adapt to the slight misalignment caused by the installation of the pump and the motor, as well as the deformation of the pump shaft under load. At the same time, the no-lubrication feature avoids the pollution of the conveyed medium by lubricant leakage, which is particularly important for the conveying of food, medicine, and other clean media. Another important application field is the electric motor industry. Electric motors are the power source of various mechanical equipment. The single diaphragm coupling is used to connect the motor shaft and the load shaft. Its compact structure and light weight do not increase too much burden on the motor, and its vibration damping performance can reduce the impact of motor vibration on the load equipment, improving the stability and service life of the entire system. In addition, the single diaphragm coupling is also widely used in the field of precision machinery, such as CNC machine tools, machining centers, and robots. These equipment require high precision and stability of motion transmission. The single diaphragm coupling can ensure precise torque transmission, and its misalignment compensation capability can avoid the impact of shaft misalignment on the machining precision. The no-lubrication feature also ensures the cleanliness of the working environment of the precision machinery, preventing lubricant from contaminating the workpieces and the machine tool guideways. In the aerospace field, the single diaphragm coupling is used in aircraft engines, auxiliary power units, and other components. Due to the harsh working environment of aerospace equipment (high temperature, high pressure, vibration, etc.), the single diaphragm coupling made of high-temperature resistant and corrosion-resistant materials can meet the requirements of reliable operation. Its light weight and compact structure are also in line with the requirements of lightweight design of aerospace equipment. In addition, the single diaphragm coupling is also used in the automotive industry (such as connecting the engine and the transmission), the wind power generation industry (connecting the wind turbine and the generator), and the marine industry (connecting the marine diesel engine and the propeller shaft), etc.
The correct selection of a single diaphragm coupling is crucial to ensure the normal operation of the transmission system, improve the reliability of the equipment, and reduce the maintenance cost. When selecting, the following key factors should be considered. Firstly, the torque transmission requirement. The rated torque of the selected single diaphragm coupling must be greater than or equal to the maximum working torque of the transmission system. It should be noted that the maximum working torque may include the starting torque of the motor, the impact torque during operation, etc. Therefore, a certain safety margin should be considered when selecting. Generally, the safety factor is 1.2-2.0, depending on the severity of the load impact. Secondly, the shaft misalignment amount. The maximum misalignment compensation capacity of the single diaphragm coupling must be greater than the actual misalignment amount of the two shafts in the system. The actual misalignment amount can be measured during installation or calculated according to the structural parameters of the equipment and the working conditions. It is necessary to ensure that the axial, radial, and angular misalignments are all within the allowable range of the coupling. Thirdly, the working speed. The maximum allowable speed of the single diaphragm coupling must be greater than the working speed of the shafts. The working speed is related to the centrifugal force generated by the coupling during operation. If the speed exceeds the allowable range, the centrifugal force will increase significantly, which may cause damage to the diaphragm or the shaft hubs. Therefore, when selecting, the linear speed of the outer edge of the diaphragm should also be considered to avoid excessive centrifugal force. Fourthly, the working environment. The working environment factors such as temperature, humidity, corrosion, and dust should be considered when selecting the material of the single diaphragm coupling. For example, in high-temperature environments, high-temperature resistant materials such as Inconel alloy should be selected; in corrosive environments, stainless steel or titanium alloy materials should be selected. Fifthly, the installation space. The size of the installation space should be considered when selecting the structure and size of the single diaphragm coupling. For applications with limited installation space, a compact flanged single diaphragm coupling or a short-length shaft hub structure can be selected. Sixthly, the cost factor. On the premise of meeting the performance requirements, the cost of the single diaphragm coupling should be considered as much as possible. Different materials and structures of couplings have different costs. For example, titanium alloy diaphragms are more expensive than stainless steel diaphragms. Therefore, a reasonable selection should be made according to the actual economic situation and application requirements.
Proper maintenance of the single diaphragm coupling is an important guarantee for its long-term stable operation and extension of its service life. The maintenance work mainly includes the following aspects. Firstly, regular inspection. Regularly inspect the appearance of the single diaphragm coupling, including the diaphragm, shaft hubs, and connecting fasteners. Check for cracks, deformation, wear, or corrosion on the diaphragm. If any of these defects are found, the diaphragm should be replaced in time to avoid sudden failure during operation. Check whether the connecting fasteners are loose. If they are loose, they should be tightened in time to ensure the reliable connection between the diaphragm and the shaft hubs. At the same time, check the alignment of the two shafts regularly. If the misalignment exceeds the allowable range, adjust the position of the equipment in time to correct the alignment. Secondly, cleaning. Regularly clean the surface of the single diaphragm coupling to remove dust, oil stains, and other impurities. Especially in dusty or corrosive environments, more frequent cleaning is required to prevent impurities from accelerating the wear and corrosion of the coupling components. When cleaning, neutral cleaning agents should be used to avoid corrosion of the diaphragm and shaft hubs. Thirdly, avoiding overload operation. The single diaphragm coupling should be operated within the rated torque range. Overload operation will cause excessive deformation of the diaphragm, leading to fatigue damage and shortening its service life. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor the load of the transmission system in real time. If overload occurs, the operation should be stopped immediately to check the cause and eliminate the fault. Fourthly, proper storage. If the single diaphragm coupling is not used immediately after purchase, it should be stored in a dry, ventilated, and clean environment to avoid moisture, corrosion, and dust pollution. The shaft hubs and diaphragms should be stored separately if necessary, and anti-rust treatment should be carried out on the surface of the metal components. Fifthly, replacement of worn components. When the diaphragm, shaft hubs, or connecting fasteners are worn or damaged to a certain extent, they should be replaced in time. When replacing the diaphragm, it is necessary to select a diaphragm of the same material and specification to ensure that the performance of the coupling is not affected. When replacing the fasteners, it is necessary to use fasteners of the same grade and specification to ensure the reliability of the connection.
With the continuous development of mechanical engineering technology, the performance requirements for couplings are getting higher and higher. The single diaphragm coupling, as a high-performance coupling, will also face new development opportunities and challenges. In the future, the development trend of single diaphragm couplings may focus on the following aspects. Firstly, the development of new materials. With the continuous emergence of new high-performance materials (such as composite materials, shape memory alloys, etc.), the application of these materials in the manufacturing of single diaphragm couplings will further improve their performance. For example, composite materials have the advantages of light weight, high strength, and corrosion resistance, which can further reduce the weight of the coupling and improve its environmental adaptability. Shape memory alloys can enable the diaphragm to automatically recover its original shape after deformation, improving the fatigue life of the coupling. Secondly, the optimization of structural design. With the help of advanced design software and simulation technology (such as finite element analysis, dynamic simulation, etc.), the structural design of the single diaphragm coupling will be more optimized. For example, optimizing the shape and thickness distribution of the diaphragm to improve its torque transmission capacity and misalignment compensation capacity; optimizing the structure of the shaft hub to improve its connection strength and installation convenience. Thirdly, the integration of intelligent technology. The integration of intelligent sensors into the single diaphragm coupling can realize real-time monitoring of its working state, such as monitoring the torque, speed, temperature, and diaphragm deformation. Through the analysis of the monitoring data, the potential faults of the coupling can be predicted in advance, realizing predictive maintenance and improving the reliability and safety of the transmission system. Fourthly, the adaptation to special working conditions. With the expansion of the application field of mechanical equipment, the single diaphragm coupling will need to adapt to more special working conditions, such as ultra-high temperature, ultra-low temperature, ultra-high speed, ultra-high pressure, and strong radiation. This will promote the continuous innovation and improvement of the single diaphragm coupling in terms of material selection, structural design, and manufacturing process.
In conclusion, the single diaphragm coupling is a kind of high-performance mechanical transmission component with simple structure, high transmission efficiency, excellent misalignment compensation capability, no need for lubrication, compact size, light weight, and good environmental adaptability. It is widely used in various fields such as industrial pumps, electric motors, precision machinery, aerospace, automobiles, wind power generation, and marine engineering. The correct selection and proper maintenance of the single diaphragm coupling are crucial to ensure the normal operation of the transmission system and extend the service life of the equipment. In the future, with the development of new materials, optimization of structural design, integration of intelligent technology, and adaptation to special working conditions, the single diaphragm coupling will have broader application prospects and play a more important role in the field of mechanical transmission. For engineering technicians, it is necessary to continuously deepen the understanding of the single diaphragm coupling, master its performance characteristics and application rules, and apply it more reasonably in practical engineering to improve the performance and reliability of mechanical equipment.
« Single Diaphragm Couplings » Post Date: 2024/4/25 , https://www.rokeecoupling.net/tags/single-diaphragm-couplings.html