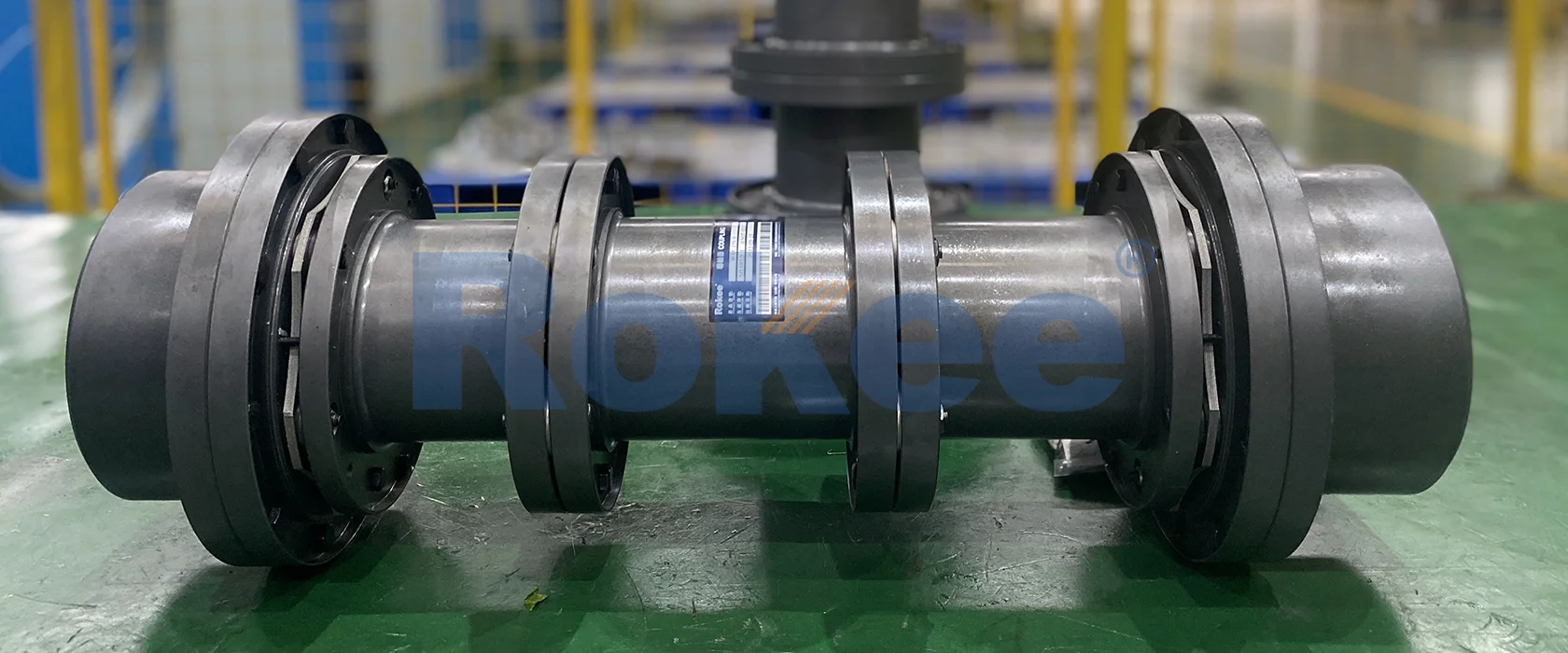

Rokee is a well-known high-quality supplier of Flexible Membrane Couplings and technical services in China, customize flexible membrane couplings according to user drawings, alternatively, if the user provides flexible membrane couplings parameters, we can select the model and design drawings for you, support wholesale and export.
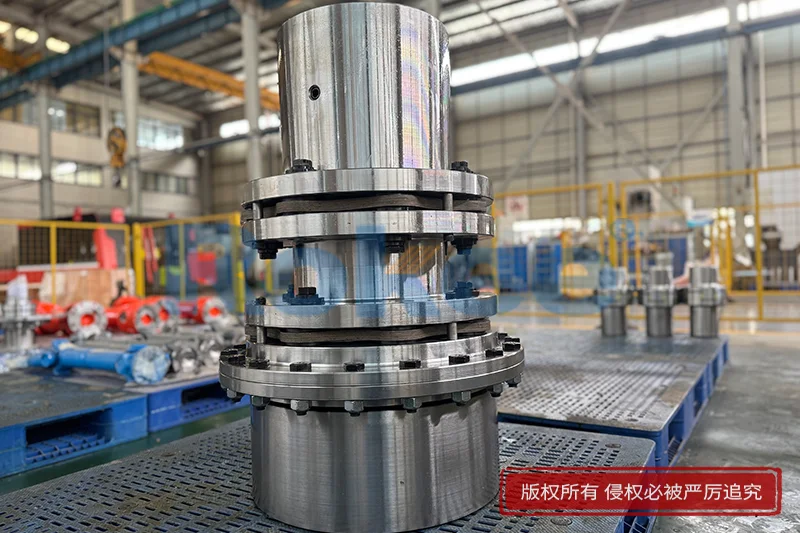
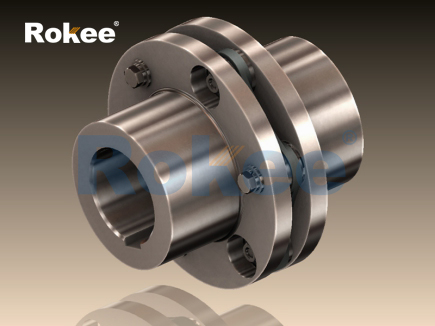




Flexible Membrane Coupling is a high-performance coupling that compensates for the relative displacement of two shafts through the elastic deformation of a metal diaphragm. Compared with traditional gear couplings or elastic couplings, it does not require lubrication, is easy to maintain, and has higher transmission accuracy, so it has been widely used in modern industrial transmission systems.
Metal diaphragm group: usually made of stainless steel, it is the core component of the coupling
Wheel hub: the two end components that connect the drive shaft and the driven shaft
Intermediate: the middle part connecting the membrane groups on both sides
Connecting bolts: used to fix various components
Axial displacement: up to ± 5mm
Radial displacement: generally up to 0.5-3mm
Angular displacement: usually 1 ° -3 °
Composite displacement: any combination of the above displacements
The diaphragm undergoes elastic deformation when transmitting torque, which ensures the transmission of force and absorbs stress caused by shaft deviation.
Maintenance free design: No lubrication required, reducing downtime and maintenance costs
High torque density: can transmit large torque under compact design
Zero backlash: ensuring high-precision transmission, suitable for servo systems
Electrical insulation: can provide electrical isolation between shafts
Long life: The fatigue life of metal film can reach more than 10 ^ 8 cycles
Good dynamic characteristics: high critical speed, low vibration
Energy industry: Steam turbines, gas turbines, wind turbines
Petrochemical industry: compressors, pump sets, fans
Shipbuilding industry: main propulsion system, auxiliary power system
Aerospace: aircraft engine test bench, auxiliary power unit
Precision Machinery: CNC Machine Tools, Semiconductor Equipment
Rail Transit: EMU Drive System
Torque demand: including rated torque and peak torque
Speed range: critical speed needs to be considered
Axis deviation type and magnitude: Determine the required compensation capability
Environmental conditions: temperature, corrosiveness, explosion-proof requirements, etc
Installation space limitations: radial and axial dimensions
Inertial matching: particularly important for high dynamic response systems
Ensure that the axis alignment accuracy is within the allowable range of the coupling
Use specialized tools for installation and avoid knocking
Tighten the bolts according to the specified torque value
Perform dynamic balance check (during high-speed applications)
Regularly check the tightening status of bolts
Monitor changes in vibration levels
Check whether the membrane has cracks or permanent deformation
Clean the surface of the coupling to prevent the accumulation of corrosive substances
As an important component of modern transmission systems, the development of Flexible Membrane Couplings will continue to drive the mechanical transmission field towards higher efficiency and reliability.
In the complex and sophisticated field of mechanical power transmission, the search for reliable, efficient, and durable coupling devices has been a persistent focus for engineers and manufacturers across industries. Among the diverse range of coupling solutions available, the flexible membrane coupling stands out as a high-performance option that has revolutionized power transmission in numerous critical applications. This advanced mechanical component leverages the elastic properties of metal materials to achieve seamless torque transfer while accommodating inherent misalignments between connected shafts, eliminating many of the limitations associated with traditional coupling designs. Unlike conventional couplings that rely on sliding parts or elastomeric elements, the flexible membrane coupling utilizes precision-engineered metal diaphragms to balance the dual requirements of rigid torque transmission and flexible deviation compensation, making it indispensable in environments where precision, reliability, and low maintenance are paramount.
At its core, the flexible membrane coupling is a type of metallic elastic coupling that transmits rotational power between two shafts through a series of thin, flexible metal diaphragms. These diaphragms, typically constructed from high-strength stainless steel or other alloy materials, are the key functional components that enable both torque transfer and misalignment compensation. The basic structure of a flexible membrane coupling generally consists of three primary parts: two hubs that attach to the driving and driven shafts, one or more sets of diaphragms, and connecting fasteners such as bolts. The hubs are designed to form a secure connection with the shafts, often through interference fits, keyway connections, or friction-based clamping mechanisms, ensuring that rotational motion from the driving shaft is efficiently transferred to the coupling assembly. The diaphragms are then fastened to the hubs in a staggered pattern using precision bolts, creating a rigid connection for torque transmission while maintaining the flexibility needed to accommodate shaft misalignments.
The design of the diaphragms themselves is a critical factor in determining the performance characteristics of the coupling. Diaphragms are typically fabricated from thin sheets of high-strength metal, with multiple sheets stacked together to form a diaphragm pack that enhances both strength and flexibility. The number of sheets in a pack can vary depending on the torque requirements and misalignment compensation needs of the application, with packs usually consisting of 4 to 12 individual sheets. These sheets are precision-machined with bolt holes and, in some cases, stress relief grooves to distribute mechanical stress evenly across the surface, minimizing the risk of fatigue failure. Two common diaphragm configurations are widely used: the link-type and the integral-type. Link-type diaphragms feature multiple separate connecting arms that link the inner and outer mounting rings, providing enhanced flexibility for compensating angular and radial misalignments. Integral-type diaphragms, by contrast, have a continuous annular structure, offering higher torsional stiffness and better suitability for high-precision, high-speed applications where minimal torsional deflection is required.
The working principle of the flexible membrane coupling is rooted in the elastic deformation of the metal diaphragms. When the driving shaft rotates, torque is transmitted to the diaphragm pack through the bolted connection between the hub and the diaphragms. As the diaphragms receive this torque, they undergo slight elastic shear deformation, which allows the rotational motion to be transferred to the driven hub and subsequently to the driven shaft. The key advantage of this design lies in the diaphragm’s ability to accommodate various types of shaft misalignment through elastic deformation without any sliding or rubbing parts. Shaft misalignments are inevitable in most mechanical systems, often resulting from manufacturing tolerances, installation errors, thermal expansion, or structural deflection during operation. These misalignments can be categorized into three main types: angular, parallel (radial), and axial misalignment. The flexible membrane coupling addresses each of these through specific deformation modes of the diaphragms.
Angular misalignment occurs when the axes of the driving and driven shafts intersect at an angle rather than being collinear. In this case, the diaphragms bend elastically to accommodate the angle between the shafts, ensuring that torque transmission remains smooth and continuous. The degree of angular misalignment that can be compensated depends on factors such as the number of diaphragms, their thickness, and their material properties. Parallel misalignment, on the other hand, arises when the shafts are offset parallel to each other without intersecting. This type of misalignment causes the diaphragms to undergo tensile and compressive deformation across their surface, absorbing the radial offset while maintaining torque transfer efficiency. Axial misalignment, which involves linear displacement along the axis of the shafts, is compensated by planar deformation of the diaphragms, allowing the shafts to move closer together or further apart without disrupting power transmission. Importantly, the elastic deformation of the diaphragms is fully reversible, meaning that the coupling returns to its original shape once the misalignment is resolved, ensuring long-term structural integrity and consistent performance.
One of the most significant advantages of the flexible membrane coupling over traditional coupling designs is its maintenance-free operation. Unlike gear couplings, which require regular lubrication to reduce friction and wear between meshing teeth, the flexible membrane coupling has no sliding or rotating contact parts that require lubrication. This eliminates the need for routine lubrication schedules, reduces maintenance costs, and prevents the risk of oil contamination in sensitive applications such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, or cleanroom environments. Additionally, the absence of lubrication means that the coupling can operate reliably in extreme temperature conditions without the risk of lubricant degradation or viscosity changes affecting performance. The operating temperature range of flexible membrane couplings is typically broad, spanning from -80°C to 300°C depending on the material used, making them suitable for both cryogenic and high-temperature applications.
Another key benefit of the flexible membrane coupling is its high transmission efficiency and precision. Due to the rigid connection between the hubs and diaphragms, there is no rotational backlash or play in the coupling, ensuring that torque and rotational speed are transmitted with minimal loss. Transmission efficiency rates of up to 99.86% are achievable, making the coupling ideal for high-power applications where energy efficiency is a priority. The zero-backlash design also makes it suitable for precision motion control systems, such as those used in CNC machine tools, servo motors, and robotics, where accurate positioning and rapid response are critical. In these applications, even minimal backlash can lead to positioning errors and reduced system performance, making the flexible membrane coupling a superior choice compared to elastomeric couplings or gear couplings that may exhibit inherent play.
The material selection for flexible membrane couplings plays a crucial role in determining their performance, durability, and suitability for specific applications. Stainless steel is the most commonly used material for diaphragms due to its excellent combination of strength, flexibility, corrosion resistance, and fatigue resistance. Austenitic stainless steels, in particular, are preferred for their high tensile strength and resistance to oxidation, making them suitable for harsh environments involving corrosive media, high temperatures, or humid conditions. For applications requiring even higher strength or temperature resistance, alloy materials such as titanium or Inconel may be used, although these materials typically come with higher manufacturing costs. The hubs of the coupling are often constructed from carbon steel, alloy steel, or aluminum alloy, depending on the torque requirements and weight constraints of the application. Aluminum alloy hubs are favored in lightweight applications such as aerospace or portable machinery, while carbon steel or alloy steel hubs are used for heavy-duty industrial applications requiring high torque capacity.
The torque capacity of flexible membrane couplings is another critical performance parameter, with values ranging from 25 N·m to over 1,000,000 N·m depending on the size, design, and material of the coupling. This wide range of torque capacity makes the coupling suitable for applications spanning from small precision machinery to large industrial equipment such as gas turbines, compressors, and marine propulsion systems. The torque transmission capability is primarily determined by the cross-sectional area of the diaphragms, the number of diaphragms in the pack, and the material’s shear strength. Engineers must carefully calculate the required torque capacity based on the application’s operating conditions, including peak torque, continuous torque, and any shock loads that may be encountered. Shock loads, which are sudden increases in torque caused by start-up, shutdown, or load fluctuations, can significantly impact the coupling’s service life. Flexible membrane couplings are designed to withstand peak torque loads up to twice the rated continuous torque, providing a safety margin against unexpected shock loads.
Vibration damping and noise reduction are additional performance benefits of flexible membrane couplings. The elastic deformation of the diaphragms helps to absorb and dampen vibrations generated by the rotating shafts, reducing the transmission of vibrations to other components in the mechanical system. This vibration damping effect not only improves the overall stability and performance of the system but also extends the service life of bearings, seals, and other sensitive components by reducing mechanical stress. Furthermore, the absence of sliding parts eliminates the noise associated with friction in gear couplings or elastomeric wear in rubber couplings, resulting in quieter operation. Noise levels are typically kept below 65 dB(A), making the coupling suitable for applications where low noise is required, such as in indoor machinery, medical equipment, or residential areas.
The versatility of flexible membrane couplings is evident in their wide range of applications across various industries. In the energy sector, they are extensively used in gas turbines, steam turbines, and generators, where they compensate for thermal expansion-induced shaft misalignments and ensure efficient power transmission. Gas turbines, in particular, benefit from the coupling’s lightweight design, high reliability, and maintenance-free operation, as these systems often operate at high speeds and temperatures with minimal access for maintenance. In the process industry, flexible membrane couplings are used in pumps, compressors, and mixers, especially in corrosive environments such as chemical processing plants or oil refineries. High-power chemical pumps, for example, rely on the coupling’s corrosion resistance and ability to handle misalignments caused by pump vibration or pipe stress.
The aerospace and defense industries also rely heavily on flexible membrane couplings for critical applications such as helicopter main rotor transmission systems and aircraft accessory drives. In these applications, the coupling’s lightweight design, high torsional stiffness, and zero backlash are essential for ensuring precise control and reliable performance under extreme operating conditions. Helicopter main rotor systems, for instance, require couplings that can transmit high torque while accommodating small misalignments and absorbing vibrations, all while maintaining a low weight to optimize fuel efficiency and maneuverability. The marine industry uses flexible membrane couplings in ship propulsion systems, where they compensate for misalignments between the engine and propeller shaft caused by hull deformation or thermal expansion, ensuring smooth and efficient power transfer in harsh marine environments.
In the manufacturing and automation sector, flexible membrane couplings are integral to CNC machine tools, robotic arms, and servo systems. CNC machine tools require high-precision torque transmission to achieve accurate cutting and machining operations, and the zero-backlash design of the coupling ensures that positional errors are minimized. Robotic arms, which operate with high speed and precision, benefit from the coupling’s lightweight design and vibration damping capabilities, allowing for smooth and precise motion control. Additionally, the coupling’s ability to accommodate misalignments reduces wear on robotic joints and extends the service life of the equipment.
The mining and冶金 industries use flexible membrane couplings in heavy-duty equipment such as crushers, grinders, and conveyor systems. These applications involve high torque loads, harsh operating conditions, and significant vibration, making the coupling’s durability, high torque capacity, and vibration damping essential. Crushers, for example, generate substantial shock loads during operation, and the coupling’s ability to withstand peak torque loads ensures reliable performance and prevents premature failure. The coupling’s maintenance-free operation is also a significant advantage in mining environments, where equipment is often located in remote areas with limited access for routine maintenance.
Proper installation and maintenance practices are essential to ensure the optimal performance and long service life of flexible membrane couplings. Before installation, it is critical to clean the shaft ends thoroughly to remove any dirt, rust, or debris that could affect the fit between the hub and the shaft. The mating surfaces of the hubs and diaphragms should also be inspected for damage, such as scratches or burrs, which could cause stress concentrations or uneven torque distribution. The alignment of the shafts should be checked using precision tools such as dial indicators or laser alignment systems to minimize initial misalignment, as excessive misalignment can lead to increased stress on the diaphragms and premature fatigue failure.
The method of hub installation depends on the type of fit between the hub and the shaft. Interference fits, which are common for high-torque applications, require the hub to be heated or the shaft to be cooled to facilitate assembly. This temperature difference assembly method is preferred over forceful installation methods such as hammering or pressing, as it avoids damaging the hub or shaft surfaces and ensures a uniform fit. When heating the hub, the temperature should be carefully controlled to avoid exceeding 400°C, as temperatures above this can cause structural changes in the metal, reducing its strength and fatigue resistance. The recommended heating temperature is typically determined based on the interference value and the material properties of the hub.
After installation, the coupling should be checked for proper bolt tightness. Bolts should be tightened in a staggered sequence using a torque wrench to ensure uniform clamping force. It is recommended to tighten the bolts to 50% of the rated torque initially, followed by a final tightening to 100% of the rated torque. This two-stage tightening process ensures that the diaphragms are evenly compressed and that there is no uneven stress distribution. Additionally, the flange clearance between the hubs should be checked to ensure it falls within the recommended range of 0.2 to 0.3 mm, allowing for thermal expansion and axial misalignment compensation.
While flexible membrane couplings are maintenance-free in terms of lubrication, regular inspection is still necessary to detect signs of wear, fatigue, or damage. It is recommended to inspect the coupling every 5000 operating hours, or more frequently in harsh operating conditions. During inspection, the diaphragms should be checked for fatigue cracks, especially around the bolt holes and stress relief grooves, as these are common areas for stress concentration. The bolts should also be inspected for tightness and signs of corrosion or wear. If cracks or damage are detected, the diaphragm pack should be replaced immediately to prevent coupling failure, which could lead to costly equipment damage or downtime.
To extend the service life of the diaphragms, a solid lubricant such as molybdenum disulfide can be applied between the diaphragm sheets. This reduces fretting wear caused by small relative movements between the sheets during operation, preventing the formation of microcracks around the bolt holes. Additionally, the surface of the diaphragms can be treated with a wear-resistant coating to enhance their durability in abrasive environments. Avoiding long-term overloading and operating within the coupling’s rated torque and misalignment limits is also critical for ensuring a long service life. Overloading can cause excessive stress on the diaphragms, leading to premature fatigue failure, while operating beyond the recommended misalignment limits can result in increased vibration and reduced coupling performance.
Despite their numerous advantages, flexible membrane couplings do have some limitations that must be considered when selecting a coupling for a specific application. One of the main limitations is their higher initial cost compared to elastomeric couplings or simple gear couplings. This higher cost is due to the precision machining required for the diaphragms and hubs, as well as the use of high-strength materials. However, the long service life, low maintenance costs, and reduced downtime associated with flexible membrane couplings often offset the higher initial investment over the lifetime of the equipment.
Another limitation is their relatively low damping capacity compared to elastomeric couplings. While the diaphragms provide some vibration damping, they are not as effective as rubber or elastomeric elements in absorbing high-amplitude vibrations. This makes them less suitable for applications with significant vibration or shock loads, unless additional damping components are incorporated into the system. Additionally, flexible membrane couplings have limited radial misalignment compensation capability compared to some other coupling types, such as universal joints or cardan shafts. For applications with large radial misalignments, a double diaphragm coupling with a central spacer may be used, as this configuration provides higher radial misalignment compensation capability than a single diaphragm coupling.
The design and optimization of flexible membrane couplings continue to evolve with advances in materials science, manufacturing technology, and computer-aided engineering. Modern design techniques such as finite element analysis (FEA) are used to simulate the stress distribution and deformation of the diaphragms under various operating conditions, allowing engineers to optimize the diaphragm shape, thickness, and bolt pattern for maximum performance and durability. FEA simulations can also predict fatigue life, enabling the design of couplings that meet specific service life requirements for critical applications.
Advances in manufacturing technology, such as precision laser cutting and CNC machining, have improved the accuracy and consistency of diaphragm production, reducing tolerances and ensuring uniform performance across batches. Laser cutting allows for complex diaphragm shapes with precise stress relief grooves, while CNC machining ensures that bolt holes are drilled with high accuracy, minimizing stress concentrations. Additionally, additive manufacturing techniques are being explored for the production of custom diaphragms with optimized geometries, allowing for further improvements in performance and weight reduction.
Materials research is also driving improvements in flexible membrane coupling performance. New alloy materials with enhanced strength, fatigue resistance, and corrosion resistance are being developed, expanding the operating range of the coupling and making it suitable for even more demanding applications. For example, advanced stainless steel alloys with higher temperature resistance are being used in gas turbine applications, while titanium alloys are being explored for lightweight aerospace applications. Additionally, surface treatment technologies such as physical vapor deposition (PVD) are being used to enhance the wear resistance and corrosion resistance of diaphragms, further extending their service life.
In conclusion, the flexible membrane coupling is a highly advanced and versatile mechanical component that has transformed power transmission in numerous industries. Its unique design, which leverages the elastic properties of metal diaphragms to achieve torque transmission and misalignment compensation, offers a combination of advantages that are unmatched by traditional coupling designs. From high-precision CNC machines to heavy-duty gas turbines, from aerospace applications to chemical processing plants, the flexible membrane coupling provides reliable, efficient, and maintenance-free performance in some of the most demanding operating conditions. While it has some limitations, ongoing advances in design, manufacturing, and materials science are continuously expanding its capabilities and applications.
As industries continue to demand higher efficiency, precision, and reliability from their mechanical systems, the flexible membrane coupling is poised to remain a critical component in power transmission technology. Its ability to balance high torque capacity, zero backlash, vibration damping, and corrosion resistance makes it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications, and its maintenance-free operation helps to reduce costs and improve productivity. Whether in energy production, manufacturing, aerospace, or marine industries, the flexible membrane coupling plays a vital role in ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of mechanical systems, contributing to the advancement of technology and industry worldwide.
« Flexible Membrane Couplings » Latest Update Date: 2026/1/20 , https://www.rokeecoupling.net/tags/flexible-membrane-couplings.html