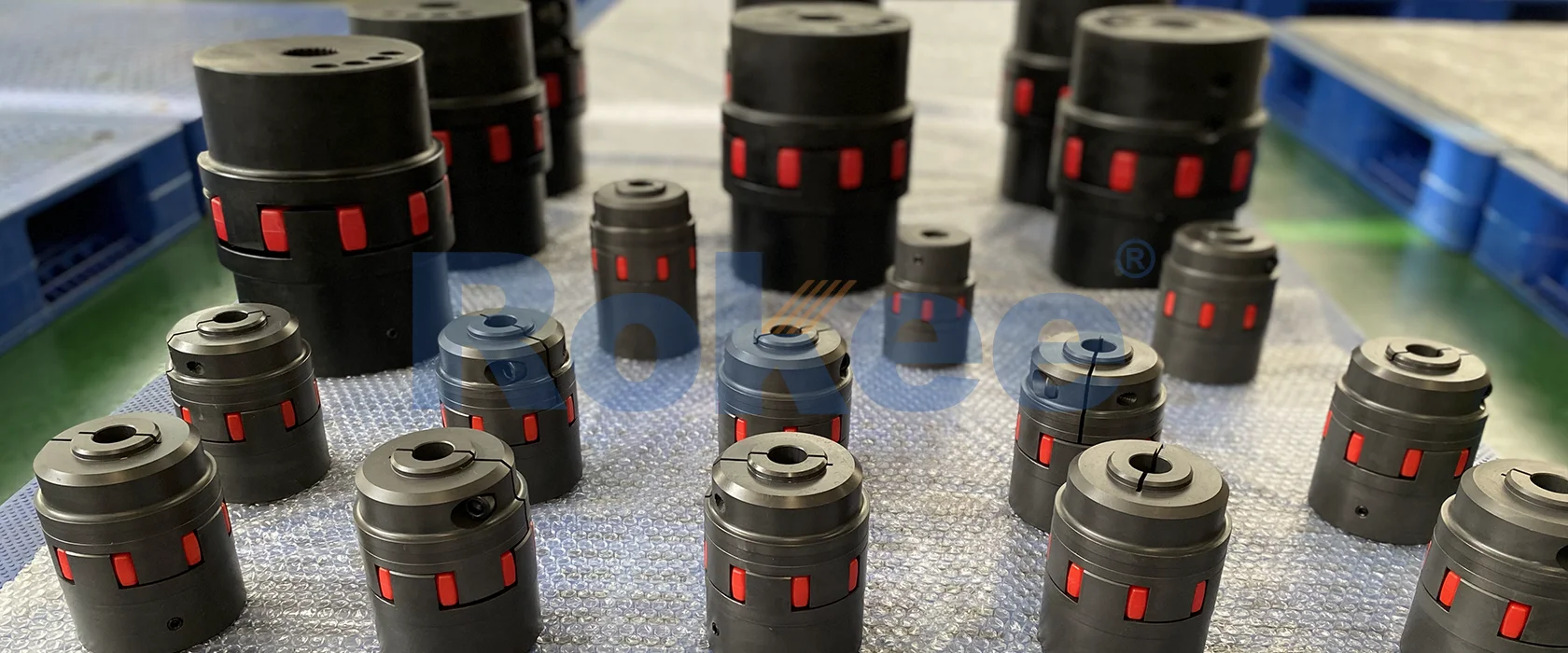

Rokee is a well-known high-quality supplier of Jaw Flexible Couplings and technical services in China, customize jaw flexible couplings according to user drawings, alternatively, if the user provides jaw flexible couplings parameters, we can select the model and design drawings for you, support wholesale and export.


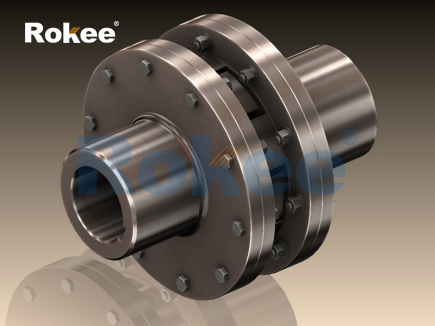

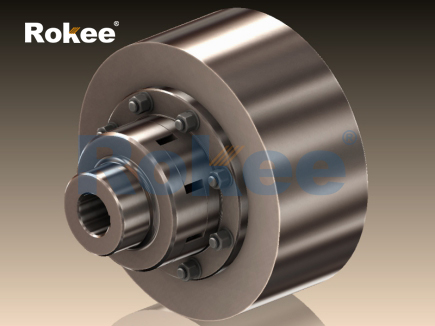


In the realm of mechanical power transmission, couplings play an indispensable role as components that connect two shafts to transmit torque while accommodating various forms of misalignment. Among the diverse types of couplings available, jaw flexible couplings have emerged as a preferred choice for numerous industrial applications due to their simplicity, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Unlike rigid couplings that demand precise alignment and offer no flexibility, jaw flexible couplings integrate a flexible element to absorb shocks, dampen vibrations, and compensate for axial, radial, and angular misalignments between connected shafts. This article delves into the fundamental principles, structural components, material selections, key advantages, application scenarios, and maintenance practices of jaw flexible couplings, providing a comprehensive understanding of their functionality and value in modern mechanical systems.
To begin with, it is essential to define the core functionality of jaw flexible couplings. A jaw flexible coupling is a type of mechanical coupling designed to transmit rotational power from a driving shaft (e.g., from a motor) to a driven shaft (e.g., to a pump, conveyor, or gearbox) while mitigating the adverse effects of shaft misalignment and reducing operational vibrations. The defining feature of this coupling type is its split design, consisting of two jaw-shaped hubs and a flexible insert (often referred to as an elastomer or spider) that fits between the jaws of the two hubs. When the driving shaft rotates, torque is transferred through the jaws of the driving hub to the flexible insert, which then transmits the torque to the jaws of the driven hub, ultimately rotating the driven shaft. This design not only ensures efficient torque transmission but also allows for a certain degree of flexibility, making the coupling adaptable to the dynamic conditions of mechanical systems.
The structural composition of jaw flexible couplings is relatively straightforward, yet each component is critical to its overall performance. The primary components include two jaw hubs, a flexible insert, and in some cases, fasteners such as set screws or keyways for securing the hubs to the shafts. The jaw hubs are typically cylindrical in shape with a series of evenly spaced, protruding jaws on one end. The number of jaws can vary depending on the coupling size and torque capacity, with common configurations ranging from three to six jaws. These hubs are mounted on the driving and driven shafts, respectively, and their jaws are positioned to interlock with the flexible insert. The flexible insert, which is the heart of the coupling’s flexibility, is designed to fit snugly between the jaws of the two hubs. It is usually made of elastic materials that can deform slightly under load, allowing for misalignment compensation and vibration absorption. In addition, some jaw flexible couplings may include a cover or shield to protect the internal components from dust, debris, and external impacts, thereby extending the coupling’s service life.
The working principle of jaw flexible couplings revolves around the interaction between the rigid jaws and the flexible insert. When the driving shaft rotates, the jaws of the driving hub exert a tangential force on the flexible insert. Since the insert is elastic, it deforms slightly to accommodate any misalignment between the two shafts and then transfers the rotational force to the jaws of the driven hub. This process ensures that torque is transmitted smoothly even when there is a small degree of axial (parallel) misalignment, radial (lateral) misalignment, or angular (tilt) misalignment between the shafts. Axial misalignment occurs when the shafts are offset along their common axis, radial misalignment when the shafts are parallel but not concentric, and angular misalignment when the shafts are not parallel but intersect at a point. The flexible insert absorbs the forces generated by these misalignments, preventing them from being transmitted to the connected equipment, which would otherwise cause excessive wear, noise, and premature failure.
Material selection is a crucial factor that determines the performance, durability, and application range of jaw flexible couplings. The jaw hubs are typically manufactured from metallic materials due to their need to withstand high torque and mechanical stress. Common materials for hubs include cast iron, steel, and aluminum. Cast iron is widely used for general-purpose applications due to its high strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Steel hubs, on the other hand, offer higher torque capacity and are suitable for heavy-duty applications where greater strength is required. Aluminum hubs are lighter in weight, making them ideal for applications where weight reduction is a priority, such as in automotive or aerospace auxiliary systems. The flexible insert, by contrast, is made from elastomeric materials that exhibit high elasticity, wear resistance, and resistance to environmental factors such as temperature, oil, and chemicals. Common elastomers used for inserts include natural rubber, nitrile rubber (NBR), neoprene, and polyurethane. Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and vibration damping but has limited resistance to oil and high temperatures. Nitrile rubber is resistant to oil and fuel, making it suitable for applications in the automotive and petroleum industries. Neoprene provides good resistance to weather, ozone, and chemicals, while polyurethane offers high wear resistance and a longer service life, making it ideal for high-speed or heavy-load applications.
Jaw flexible couplings offer a multitude of advantages that make them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications. One of the key advantages is their ability to compensate for multiple types of shaft misalignment, as discussed earlier. This flexibility eliminates the need for precise shaft alignment during installation, reducing installation time and labor costs. Additionally, the flexible insert acts as a vibration damper, absorbing operational vibrations generated by the driving motor or other rotating components. This vibration damping not only reduces noise levels in the workplace but also minimizes wear and tear on the connected equipment, extending the service life of motors, pumps, gearboxes, and other mechanical components. Another significant advantage is their simple design and ease of installation and maintenance. Unlike complex couplings that require specialized tools or expertise for installation, jaw flexible couplings can be easily mounted and dismounted using basic tools. The flexible insert is also a replaceable component, meaning that when it becomes worn or damaged, it can be replaced without replacing the entire coupling, resulting in lower maintenance costs and downtime.
Furthermore, jaw flexible couplings exhibit high torque transmission efficiency. The rigid jaws and snug-fitting insert ensure that most of the torque generated by the driving shaft is transmitted to the driven shaft, with minimal power loss. This efficiency is particularly important in applications where energy conservation is a priority. Additionally, these couplings are compact in size, making them suitable for applications where space is limited. They also have a relatively low weight, which reduces the overall load on the mechanical system. Another advantage is their ability to absorb shock loads. In industrial processes where sudden load changes or shock impacts are common (e.g., in mining or construction equipment), the flexible insert acts as a buffer, absorbing the shock and preventing it from damaging the connected shafts and equipment. Finally, jaw flexible couplings are cost-effective compared to other types of flexible couplings such as disc couplings or gear couplings. Their simple design, low material costs, and ease of maintenance make them an economical choice for both small-scale and large-scale industrial applications.
Due to their numerous advantages, jaw flexible couplings find applications in a wide range of industries and mechanical systems. One of the most common applications is in the manufacturing industry, where they are used to connect motors to various types of machinery such as conveyors, mixers, compressors, and packaging equipment. In conveyor systems, for example, jaw flexible couplings transmit torque from the drive motor to the conveyor belt pulley, while compensating for any misalignment between the motor shaft and the pulley shaft. They also absorb vibrations generated by the motor, ensuring smooth operation of the conveyor system. In the automotive industry, jaw flexible couplings are used in auxiliary systems such as power steering pumps, water pumps, and alternators. The lightweight aluminum hubs and oil-resistant elastomeric inserts make them suitable for these applications, where space and weight are critical factors.
The pumping industry is another major user of jaw flexible couplings. Pumps, whether centrifugal, positive displacement, or submersible, require efficient torque transmission from the motor to the pump impeller. Jaw flexible couplings are ideal for this application because they can compensate for the misalignment that may occur due to the installation of the pump and motor on different bases or due to thermal expansion and contraction during operation. They also absorb vibrations, reducing noise and extending the service life of the pump and motor. In the HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) industry, jaw flexible couplings are used in air handlers, fans, and chillers. These couplings ensure reliable torque transmission while minimizing vibrations, which is essential for maintaining a comfortable and quiet environment in commercial and residential buildings.
Other applications of jaw flexible couplings include the agricultural industry, where they are used in farm machinery such as tractors, harvesters, and irrigation pumps. The rugged design and ability to absorb shock loads make them suitable for the harsh conditions of agricultural operations. In the marine industry, they are used in small to medium-sized boats to connect the engine to the propeller shaft, where they compensate for misalignment caused by hull flexing and absorb engine vibrations. They are also used in renewable energy systems such as small wind turbines and solar water pumps, where their efficiency and reliability are critical for maximizing energy output.
Despite their simplicity and reliability, jaw flexible couplings require proper maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Regular maintenance practices include inspection, lubrication (in some cases), and replacement of worn components. The first step in maintenance is regular visual inspection of the coupling components. This inspection should check for signs of wear or damage to the flexible insert, such as cracks, tears, or hardening of the elastomer. Hardening of the insert is often caused by exposure to high temperatures or chemicals and can reduce its flexibility, compromising the coupling’s ability to compensate for misalignment and absorb vibrations. The jaws of the hubs should also be inspected for signs of wear, such as chipping or deformation, which can affect torque transmission.
In addition to visual inspection, it is important to check the alignment of the connected shafts periodically. While jaw flexible couplings can compensate for small degrees of misalignment, excessive misalignment can put additional stress on the flexible insert, leading to premature failure. Shaft alignment can be checked using simple tools such as a straightedge and feeler gauge for basic alignment, or more precise tools such as laser alignment systems for critical applications. If excessive misalignment is detected, the shafts should be realigned to within the coupling’s specified limits. Lubrication is another maintenance practice that may be required for some types of jaw flexible couplings. While many modern jaw couplings are maintenance-free due to the use of self-lubricating elastomeric inserts, some couplings with metallic components may require periodic lubrication to reduce friction and wear. It is important to use the correct type of lubricant as specified by the coupling’s design requirements, as using the wrong lubricant can damage the elastomeric insert.
Replacement of the flexible insert is a key maintenance task for jaw flexible couplings. The insert is the most wear-prone component, and its service life depends on factors such as operating temperature, torque load, misalignment, and environmental conditions. As a general rule, the insert should be replaced if signs of wear or damage are detected, or after a specified period of operation as recommended by the coupling’s design guidelines. Replacing the insert is a simple process that involves removing the fasteners securing the hubs to the shafts (if necessary), separating the hubs, removing the old insert, and installing a new one. It is important to ensure that the new insert is the correct size and material for the coupling, as using an incompatible insert can affect the coupling’s performance and safety.
When selecting a jaw flexible coupling for a specific application, several factors need to be considered to ensure optimal performance. The first and most important factor is the torque capacity of the coupling. The coupling must be able to transmit the maximum torque generated by the driving shaft without failure. The torque capacity of a jaw flexible coupling depends on factors such as the size of the hubs, the number of jaws, and the material of the insert. It is important to select a coupling with a torque capacity that exceeds the maximum operating torque of the system to provide a safety margin. Another important factor is the type and amount of misalignment that the coupling will need to compensate for. Different couplings have different misalignment limits, and it is important to select a coupling that can accommodate the expected misalignment in the application. The operating speed of the system is also a critical factor, as high-speed applications require couplings that can withstand centrifugal forces and maintain their balance. The coupling’s maximum allowable speed should exceed the system’s operating speed to prevent vibration and premature failure.
Environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals or corrosive substances also influence the selection of a jaw flexible coupling. For high-temperature applications, it is important to select an insert material that can withstand the elevated temperatures without hardening or degrading. For applications exposed to oil, fuel, or chemicals, an oil-resistant elastomer such as nitrile rubber or polyurethane should be used. In corrosive environments, the hubs should be made of corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel or aluminum. The size and space constraints of the application are also important considerations. The coupling must fit within the available space, and its weight should not exceed the load capacity of the mechanical system. Finally, cost is a factor that cannot be overlooked. While jaw flexible couplings are generally cost-effective, the cost can vary depending on the size, material, and torque capacity. It is important to balance cost with performance requirements to select a coupling that meets the application’s needs without unnecessary expenditure.
In conclusion, jaw flexible couplings are versatile and reliable components that play a critical role in mechanical power transmission systems. Their simple design, ability to compensate for misalignment, vibration damping capabilities, and cost-effectiveness make them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications. By understanding the structural components, working principles, material selections, advantages, applications, maintenance practices, and selection criteria of jaw flexible couplings, engineers and maintenance professionals can make informed decisions when selecting and maintaining these couplings, ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of mechanical systems. As industrial technology continues to advance, jaw flexible couplings are likely to remain a staple in power transmission due to their proven performance and adaptability to evolving application requirements. Whether in manufacturing, automotive, pumping, HVAC, or agricultural applications, jaw flexible couplings contribute to the smooth, efficient, and safe operation of machinery, making them an indispensable component in the modern industrial landscape.
« Jaw Flexible Couplings » Post Date: 2024/4/25 , https://www.rokeecoupling.net/tags/jaw-flexible-couplings.html