
Rokee is a well-known high-quality supplier of Metallic Disc Couplings and technical services in China, customize metallic disc couplings according to user drawings, alternatively, if the user provides metallic disc couplings parameters, we can select the model and design drawings for you, support wholesale and export.






In the complex ecosystem of industrial power transmission, couplings act as the vital link between rotating shafts, facilitating torque transfer while addressing misalignments and mitigating operational stresses. Among the array of coupling solutions, metallic disc couplings stand out as a robust and precise option, favored in high-demand applications where reliability, torque density, and resistance to extreme conditions are non-negotiable. Distinguished by their use of thin, rigid metallic discs as the flexible element, these couplings outperform many traditional alternatives by eliminating the need for lubrication and avoiding the degradation issues associated with rubber or polymer components. This article explores the structural design, operational mechanisms, material selection criteria, key performance advantages, and diverse industrial applications of metallic disc couplings, highlighting their indispensable role in optimizing the efficiency and durability of modern rotating machinery.
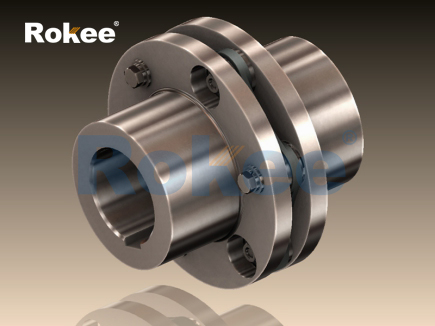
The structural integrity and performance of metallic disc couplings are rooted in their meticulously engineered components and configuration. A standard metallic disc coupling comprises three essential parts: two shaft hubs (connecting to the driving and driven shafts) and a set of metallic discs that serve as the flexible torque-transmitting medium. The hubs are precision-manufactured to ensure a secure, slip-free connection with the shafts, employing techniques such as keyway fitting, spline connection, or interference fit—each tailored to the specific torque requirements and shaft dimensions of the application. The metallic discs, the defining feature of this coupling type, are typically thin, flat, and circular, fabricated from high-strength metal alloys. These discs are often designed with strategic perforations, slots, or a series of concentric rings to balance flexibility (for misalignment compensation) and structural rigidity (for torque transmission).
A critical design consideration is the arrangement and quantity of metallic discs. Single-disc configurations are compact and cost-effective, suitable for applications with moderate misalignment demands and lower torque loads. In contrast, multi-disc assemblies—comprising two or more discs separated by spacers or washers—offer enhanced torsional stiffness, higher torque capacity, and superior misalignment compensation. The spacing between discs in multi-disc designs also helps to distribute stress evenly across the entire assembly, reducing the risk of fatigue failure. Additionally, the thickness and diameter of the discs are precisely calibrated based on the application’s operational parameters: thicker discs enhance torque-bearing capacity but reduce flexibility, while thinner discs improve misalignment accommodation but limit torque transmission. This delicate balance between flexibility and strength is a cornerstone of metallic disc coupling design, ensuring optimal performance under specific operating conditions.
The method of attaching the metallic discs to the hubs is another key design aspect that influences performance and maintainability. Common attachment techniques include bolted connections, riveted joints, and laser welding. Bolted connections are the most prevalent due to their ease of assembly and disassembly, allowing for straightforward replacement of discs during maintenance without removing the entire coupling. Riveted joints offer a more permanent and robust connection, eliminating the risk of bolt loosening under high vibration but limiting the ability to service individual components. Laser welding, a advanced attachment method, creates a seamless bond between the discs and hubs, resulting in a compact, high-strength assembly with minimal weight. However, this method is more costly and requires specialized equipment, making it suitable for high-performance, low-weight applications such as aerospace and racing.
The primary function of a metallic disc coupling is to transmit torque from the driving shaft to the driven shaft while accommodating three primary types of misalignment: angular misalignment (shafts inclined at an angle to each other), parallel misalignment (shafts offset horizontally), and axial displacement (shafts moving toward or away from each other). The metallic discs achieve this through elastic deformation—a phenomenon where the discs bend or twist slightly under load, absorbing misalignment without transferring excessive stress to the shafts or adjacent components. When torque is applied, the discs undergo torsional deformation, efficiently transferring rotational force from one hub to the other. Simultaneously, any misalignment between the shafts causes the discs to flex elastically, maintaining torque transmission while minimizing mechanical stress.
Unlike rigid couplings, which demand precise shaft alignment and transmit significant axial and radial forces to bearings and seals, metallic disc couplings isolate these forces through the elastic deformation of the discs. This force isolation reduces wear and tear on critical components such as bearings, seals, and shaft journals, extending the overall lifespan of the mechanical system. Another key operational feature is the minimal backlash of metallic disc couplings. Backlash— the clearance between mating components—is virtually eliminated due to the rigid connection between the discs and hubs, making these couplings ideal for applications requiring precise positioning and synchronization, such as CNC machine tools, robotics, and automated production lines. The absence of backlash ensures immediate response to changes in rotational speed or direction, enhancing the accuracy and repeatability of the system.
Torsional vibration damping is an additional operational benefit of metallic disc couplings. Torsional vibrations, common in rotating machinery such as engines, pumps, and compressors, can cause noise, reduce efficiency, and lead to premature component failure. The metallic discs, due to their inherent material properties and geometric design, act as a torsional spring, absorbing and dissipating vibrational energy. This damping capability is particularly effective in applications with variable speed operation or intermittent loads, where vibrations are more pronounced. Unlike elastic couplings that use rubber or polymer elements— which degrade over time and lose damping performance—metallic discs maintain consistent vibration damping characteristics over their service life, ensuring long-term reliability.
Material selection is a critical factor in determining the performance, durability, and application suitability of metallic disc couplings. The metallic discs, being the primary load-bearing and flexible component, are fabricated from high-strength, corrosion-resistant alloys capable of withstanding repeated elastic deformation without fatigue. The most commonly used materials for discs include stainless steel, carbon steel alloys, titanium, and nickel-based superalloys. Each material offers unique properties that make it suitable for specific operating environments and performance requirements.
Stainless steel is the most widely used material for metallic disc couplings, owing to its excellent combination of strength, flexibility, and corrosion resistance. Austenitic stainless steels, such as 304 and 316, are particularly popular due to their high ductility, resistance to oxidation, and compatibility with a wide range of chemicals. These properties make them ideal for applications in harsh environments, including chemical processing plants, marine equipment, and food processing facilities. Ferritic stainless steels, another common grade, offer higher thermal conductivity and lower cost but are less corrosion-resistant than austenitic grades, making them suitable for dry, moderate-temperature applications such as general industrial machinery.
Carbon steel alloys, such as S45C and 4140, are used in applications requiring high torque capacity and torsional stiffness. These alloys offer excellent strength and durability at a lower cost than stainless steel, making them suitable for heavy-duty industrial applications such as mining equipment, steel mills, and large-scale conveyors. However, carbon steel is prone to corrosion, so couplings fabricated from this material are often coated with protective finishes (such as galvanization or paint) for use in outdoor or humid environments.
Titanium is a premium material used in high-performance, low-weight applications. With an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, titanium is ideal for aerospace, automotive racing, and unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) applications where weight reduction is critical. Additionally, titanium exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, even in aggressive environments such as saltwater and acidic solutions, and can withstand high temperatures up to 500°C. However, the high cost of titanium limits its use to specialized applications where its unique properties are essential.
Nickel-based superalloys, such as Inconel and Hastelloy, are reserved for extreme operating conditions. These alloys can withstand temperatures exceeding 1000°C and are highly resistant to corrosion from acids, alkalis, and molten metals. This makes them suitable for use in petrochemical plants, nuclear power facilities, and high-temperature industrial furnaces. Nickel-based alloys also offer exceptional fatigue resistance, ensuring long-term reliability in applications with high cyclic loads and extreme temperature fluctuations.
The hubs of metallic disc couplings are typically fabricated from carbon steel, alloy steel, or aluminum. Carbon steel and alloy steel are preferred for heavy-duty applications due to their high strength, while aluminum is used in lightweight applications such as aerospace and portable machinery, thanks to its low density and good thermal conductivity.
Metallic disc couplings offer a range of performance advantages that make them a superior choice over other coupling types in many industrial applications. One of the most significant advantages is their exceptional durability and long service life. Unlike elastic couplings that rely on rubber or polymer components— which degrade over time due to heat, chemicals, or mechanical stress—metallic discs are resistant to wear, tear, and environmental degradation. This results in a longer service life and reduced maintenance requirements, lowering the total cost of ownership for end-users.
High torque capacity is another key advantage. Metallic discs, fabricated from high-strength alloys, can transmit significantly higher torques than elastic couplings of the same size. This makes metallic disc couplings suitable for heavy-duty applications such as industrial motors, pumps, compressors, and conveyors, where reliable high-torque transmission is essential. Additionally, metallic disc couplings operate with high efficiency, as the rigid connection between components and the absence of sliding or rolling elements minimize energy loss during torque transmission. This efficiency translates to lower energy consumption and reduced operational costs.
Superior misalignment compensation is a defining feature of metallic disc couplings. Depending on the design, these couplings can accommodate angular misalignments up to 4 degrees, parallel misalignments up to 3 millimeters, and axial displacements up to 20 millimeters. This flexibility eliminates the need for precise shaft alignment during installation, reducing setup time and labor costs. Furthermore, the ability to absorb misalignments reduces stress on bearings, seals, and other components, extending their service life and minimizing unplanned downtime.
Resistance to harsh operating conditions is another critical advantage. Metallic discs are unaffected by extreme temperatures (ranging from -50°C to 1000°C, depending on the material), chemicals, oils, and solvents. This makes them suitable for use in a wide range of environments, from freezing cold storage facilities to high-temperature industrial furnaces and corrosive chemical processing plants. Unlike elastic couplings that can melt, harden, or swell in extreme conditions, metallic disc couplings maintain consistent performance, ensuring reliability even in the most challenging environments. Additionally, metallic disc couplings are non-lubricated, eliminating the need for regular lubrication and reducing the risk of contamination in sensitive applications such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and cleanrooms.
Finally, metallic disc couplings offer precise torque transmission with minimal backlash. This precision is essential for applications requiring accurate positioning and synchronization, such as robotics, CNC machine tools, and automated assembly lines. The absence of backlash ensures that the driven shaft responds instantly to changes in the driving shaft’s rotation, improving the overall accuracy and productivity of the system.
Due to their robust performance and versatility, metallic disc couplings are employed across a wide range of industries. One of the primary applications is in the power generation sector, where they are used in gas turbines, steam turbines, and generators. In these applications, metallic disc couplings transmit high torques while accommodating misalignments and damping torsional vibrations, ensuring the reliable operation of power generation equipment. Their resistance to high temperatures and corrosion also makes them suitable for use in nuclear power plants, where they operate in harsh, radioactive environments.
The aerospace industry is another major user of metallic disc couplings. In aircraft engines, auxiliary power units (APUs), and flight control systems, these couplings transmit torque between rotating components while minimizing weight. The high strength-to-weight ratio of titanium and aluminum disc couplings makes them ideal for aerospace applications, where weight reduction directly impacts fuel efficiency and flight performance. Additionally, their resistance to extreme temperatures and vibration damping capabilities ensure the reliability of critical aircraft systems during flight.
In the chemical and petrochemical industry, metallic disc couplings are used in pumps, compressors, agitators, and mixers. These applications require couplings that can withstand corrosive chemicals, high pressures, and extreme temperatures. Stainless steel and nickel-based disc couplings are particularly suitable here, as their corrosion-resistant properties ensure long-term reliability and prevent contamination of process fluids. The non-lubricated design of metallic disc couplings also eliminates the risk of lubricant leakage, which is critical in chemical processing applications where contamination can have severe safety and quality consequences.
The automotive industry utilizes metallic disc couplings in high-performance vehicles, such as racing cars, electric vehicles (EVs), and hybrid vehicles. In racing cars, lightweight titanium or aluminum disc couplings transmit high torques from the engine to the transmission, improving acceleration and overall performance. In EVs and hybrids, these couplings are used in the drivetrain to connect the electric motor to the wheels, ensuring efficient torque transmission and reliable operation. Their vibration damping capabilities also help to reduce noise and improve ride comfort in electric vehicles.
Other key applications include machine tools, robotics, material handling equipment, and marine propulsion systems. In machine tools such as CNC lathes and milling machines, metallic disc couplings ensure precise torque transmission and minimal backlash, enabling accurate cutting and machining operations. In robotics, these couplings facilitate smooth, precise movement of robotic arms, improving the accuracy and repeatability of tasks such as assembly and welding. In material handling equipment—such as conveyors, lifts, and hoists—metallic disc couplings transmit high torques while accommodating misalignments, ensuring reliable operation in harsh industrial environments. In marine propulsion systems, corrosion-resistant stainless steel disc couplings are used to connect the engine to the propeller, withstanding the corrosive effects of saltwater and ensuring reliable performance at sea.
Metallic disc couplings have solidified their position as a high-performance, reliable solution for power transmission in diverse industrial applications. Their unique design—featuring thin, high-strength metallic discs as the flexible element—offers a compelling combination of durability, high torque capacity, superior misalignment compensation, resistance to harsh conditions, and precise torque transmission. The careful selection of materials, from cost-effective stainless steel to premium titanium and nickel-based alloys, ensures that these couplings can be tailored to meet the specific requirements of any application, from general industrial machinery to high-performance aerospace systems.
As industrial machinery becomes increasingly complex and demands higher levels of efficiency and reliability, the role of metallic disc couplings will continue to expand. Their ability to operate in extreme conditions, reduce maintenance costs, and improve energy efficiency makes them a cost-effective choice for a wide range of industries, including power generation, aerospace, chemical processing, and automotive. With ongoing advancements in material science and manufacturing technology—such as the development of lighter, stronger alloys and more precise machining techniques—metallic disc couplings are poised to become even more versatile and efficient, further enhancing their value in modern industrial systems. Whether in a large-scale power plant, a high-speed racing car, or a precision robotic assembly line, metallic disc couplings play a critical role in ensuring the smooth, reliable operation of rotating machinery, making them an indispensable component of the global industrial infrastructure.
« Metallic Disc Couplings » Post Date: 2024/4/25 , https://www.rokeecoupling.net/tags/metallic-disc-couplings.html