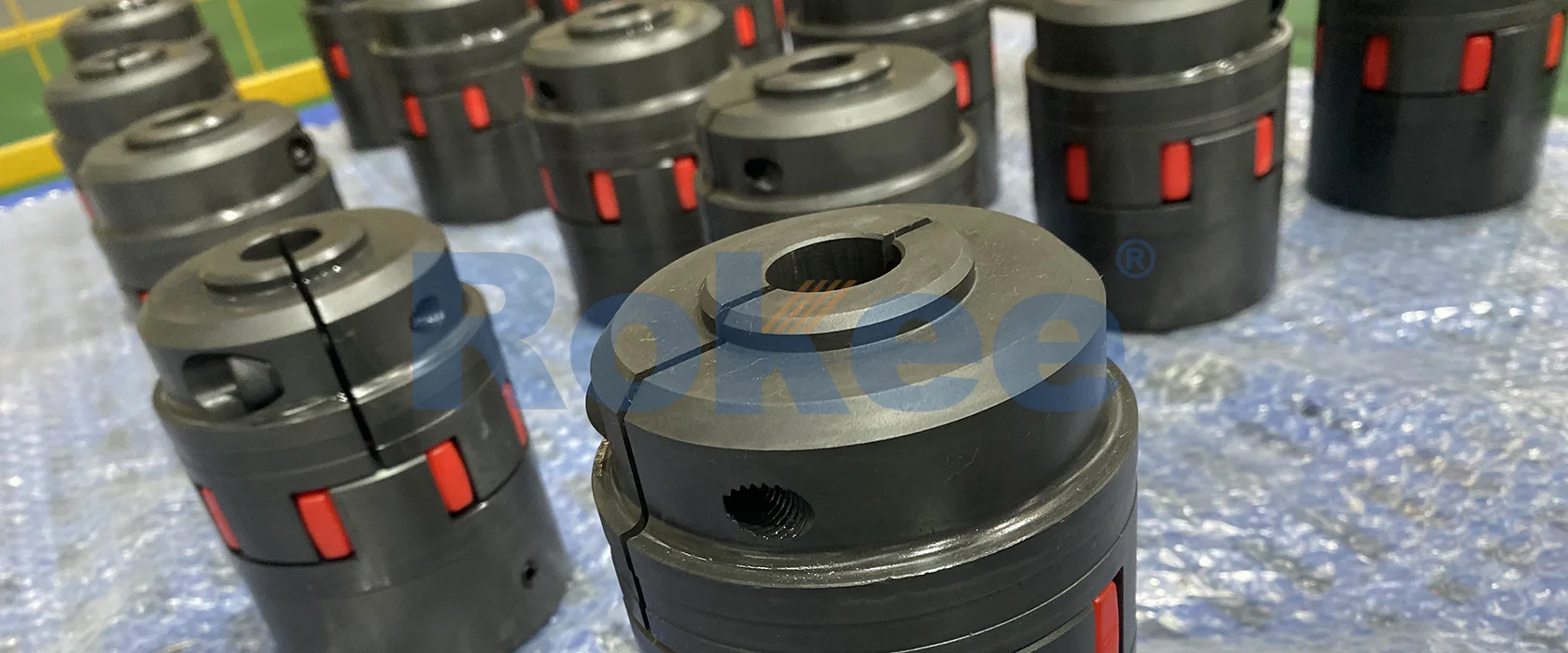

Rokee is a well-known high-quality supplier of Multi Jaw Couplings and technical services in China, customize multi jaw couplings according to user drawings, alternatively, if the user provides multi jaw couplings parameters, we can select the model and design drawings for you, support wholesale and export.


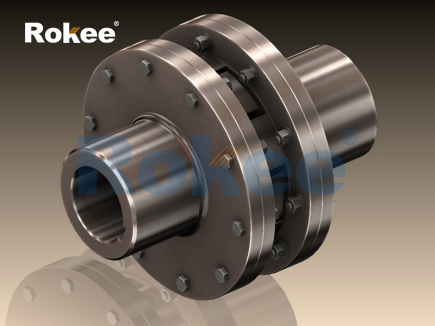

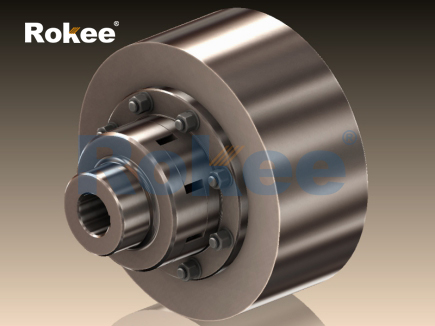


In the domain of mechanical power transmission, couplings are indispensable components that bridge rotating shafts, enabling torque transfer while mitigating the adverse effects of misalignment, vibration, and shock loads. Among the various coupling technologies available, the multi jaw coupling has emerged as a versatile and cost-effective solution, widely adopted across industrial, commercial, and even some specialized applications. Distinguished by its modular design, which combines metal jaws with an elastic insert, the multi jaw coupling balances rigidity for efficient torque transmission with flexibility for accommodating misalignments. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of multi jaw couplings, exploring their structural composition, operational principles, material characteristics, key applications, installation and maintenance procedures, technological advancements, and inherent limitations, aiming to offer a holistic understanding of this critical mechanical component.
The fundamental functionality of a multi jaw coupling is rooted in its unique structural design, which consists of three core components: two metal hubs (or flanges) with evenly spaced radial jaws, and an elastic insert (often referred to as a spider or cushion) that fits between the jaws of the two hubs. The hubs are typically machined with a specific number of jaws—common configurations include 3-jaw, 4-jaw, 6-jaw, and 8-jaw designs—with the number of jaws influencing the coupling’s torque capacity and flexibility. The elastic insert, which is the key flexible element, features corresponding notches or lobes that interlock with the jaws of both hubs. When the driving shaft rotates, torque is transmitted from the driving hub to the elastic insert via the jaw-insert interface. The insert deforms elastically to accommodate minor misalignments between the driving and driven shafts, then transfers the rotational force to the driven hub, thereby driving the driven shaft. This elastic deformation is reversible, ensuring that the insert maintains its shape and performance over repeated cycles of operation.
A defining feature of multi jaw couplings is the synergy between the rigid metal hubs and the flexible elastic insert. Unlike rigid couplings that offer no misalignment compensation, or fully elastic couplings that rely solely on polymer materials for torque transmission, multi jaw couplings leverage the strength of metal for torque bearing and the elasticity of the insert for misalignment accommodation and vibration damping. This combination results in several key performance advantages: high torque transmission efficiency (typically above 98%), moderate misalignment tolerance, effective vibration absorption, and simple installation and replacement of components. Additionally, the interlocking design of the jaws and insert ensures a positive drive, eliminating slip between components and ensuring precise torque transfer—an essential feature in applications requiring accurate speed synchronization.
The structural design of multi jaw couplings can be further categorized based on the type of hub connection and insert configuration. Hub designs include split hubs and solid hubs: split hubs feature a two-piece construction that allows for installation without removing the connected shafts, simplifying maintenance and reducing downtime, while solid hubs are a one-piece design that offers higher rigidity and torque capacity but requires shaft removal for installation. The insert, meanwhile, can be designed with different cross-sections, such as cylindrical, rectangular, or curved lobes, each optimized for specific performance characteristics. For example, curved lobe inserts provide greater flexibility and vibration damping, while rectangular lobe inserts offer higher torque capacity. Some inserts also feature a central bore to reduce weight and improve heat dissipation, particularly beneficial in high-speed applications. The hubs are typically machined with keyways, splines, or set screws to ensure a secure connection to the shafts, with precision machining ensuring tight tolerances between the jaws and the insert.
Material selection is a critical factor that determines the performance, durability, and application range of multi jaw couplings. The metal hubs, which bear the primary torque load, are commonly manufactured from high-strength materials such as carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, or aluminum alloy. Carbon steel is the most widely used material for hubs due to its excellent strength-to-cost ratio, making it suitable for most industrial applications with moderate torque requirements. Alloy steel, which is reinforced with elements such as chromium, nickel, or molybdenum, offers higher tensile strength and fatigue resistance, making it ideal for high-torque applications such as heavy-duty machinery. Stainless steel hubs are preferred in corrosive environments, such as marine, chemical processing, or food industry applications, due to their superior corrosion resistance. Aluminum alloy hubs, though less strong than steel, are lightweight and offer good thermal conductivity, making them suitable for low-torque, high-speed applications such as electric motors or small pumps.
The elastic insert, being the flexible and vibration-damping element, is typically made from polymer materials that combine elasticity, wear resistance, and resistance to environmental factors. The most commonly used materials for inserts include nitrile rubber (NBR), ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), polyurethane (PU), and silicone rubber. Nitrile rubber is widely used due to its excellent oil and fuel resistance, making it suitable for automotive and industrial applications where exposure to petroleum-based fluids is common. EPDM rubber offers superior resistance to weathering, ozone, and high temperatures, making it ideal for outdoor or high-temperature applications. Polyurethane inserts provide higher hardness and wear resistance than rubber, offering longer service life in applications with high torque or frequent shock loads. Silicone rubber, meanwhile, offers the widest temperature range (-60°C to 250°C) and excellent resistance to extreme environments, making it suitable for specialized applications such as aerospace or high-temperature industrial processes. Additives such as antioxidants, plasticizers, and reinforcing fibers are often incorporated into the insert materials to enhance their performance and extend their service life.
The versatility of multi jaw couplings, stemming from their balanced performance and flexible design, makes them suitable for a wide range of applications across diverse industries. One of the primary application areas is industrial machinery, where they are used to connect motors, pumps, compressors, fans, conveyors, and gearboxes. In pump systems, for example, multi jaw couplings accommodate the minor misalignments between the motor and pump shafts caused by thermal expansion or installation tolerances, reducing wear on the pump’s bearings and seals. In conveyor systems, their vibration damping capabilities absorb the shock loads generated during startup and material transfer, ensuring smooth operation and preventing damage to the conveyor components. Compressors, particularly those used in refrigeration or air conditioning systems, benefit from the oil resistance of nitrile rubber inserts, which prevent degradation from lubricants used in the compressor.
The automotive and transportation industry is another major user of multi jaw couplings. They are employed in the transmission systems of light commercial vehicles, agricultural machinery (such as tractors and harvesters), and construction equipment (such as excavators and loaders). In these applications, the coupling’s ability to absorb shock loads and accommodate misalignments is critical, as the machinery operates in harsh conditions with uneven terrain and frequent start-stop cycles. Multi jaw couplings are also used in electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid vehicles, where their lightweight design (when using aluminum hubs) and high efficiency contribute to improving the vehicle’s energy efficiency and range.
The food and beverage industry and pharmaceutical industry also utilize multi jaw couplings, particularly those with stainless steel hubs and food-grade rubber or polyurethane inserts. The stainless steel construction ensures resistance to corrosion from cleaning chemicals, while the food-grade inserts prevent contamination of products. These couplings are used in processing equipment such as mixers, blenders, and conveyors, where hygiene and reliability are paramount. Additionally, multi jaw couplings find applications in the renewable energy sector, such as connecting generators to wind turbines or small hydroelectric turbines, where their vibration damping capabilities help protect sensitive electrical components from mechanical stress.
Proper installation is essential to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of multi jaw couplings. The first and most critical step is the accurate alignment of the driving and driven shafts. While multi jaw couplings can accommodate moderate misalignments (typically up to 1.5 degrees angular misalignment and 0.5 mm radial misalignment, depending on the design), excessive misalignment will cause uneven stress on the elastic insert, leading to premature wear, cracking, or failure. Precision alignment tools, such as laser alignment systems or dial indicators, should be used to ensure that the shafts are aligned within the manufacturer’s recommended tolerances. It is important to check both static alignment (when the machinery is stationary) and dynamic alignment (when the machinery is operating at full speed), as thermal expansion during operation can alter the alignment of the shafts.
The next step in installation is the mounting of the hubs onto the shafts. For solid hubs, this typically involves sliding the hub onto the shaft and securing it with a key and set screws or an interference fit. For split hubs, the two halves of the hub are clamped around the shaft and fastened with bolts, eliminating the need to remove the shaft from the machinery. Once the hubs are installed, the elastic insert is placed between the jaws of the two hubs, ensuring that it fits snugly without being compressed excessively. Excessive compression of the insert can lead to increased friction, heat generation, and reduced flexibility. Finally, the coupling assembly should be inspected to ensure that there is no interference between the coupling components and other parts of the machinery, and that the shafts rotate freely without binding or excessive vibration.
Regular maintenance is crucial to prevent unexpected failures and extend the service life of multi jaw couplings. The primary maintenance task is the periodic inspection of the elastic insert, as it is the wear component of the coupling. Inspections should focus on signs of wear, such as cracking, tearing, hardening, softening, or deformation of the insert. If any of these signs are detected, the insert should be replaced immediately to avoid damage to the hubs or shafts. The hubs and their fasteners (bolts, set screws) should also be inspected regularly to ensure that they are tight and free from damage. Loose fasteners can cause excessive vibration, misalignment, and premature wear of the insert. In corrosive environments, the hubs should be inspected for signs of corrosion, and any affected components should be cleaned, treated, or replaced as necessary.
Another important maintenance practice is the lubrication of the coupling components, although most multi jaw couplings are designed to be maintenance-free due to the self-lubricating properties of the elastic insert. However, in applications where the coupling is exposed to excessive dust, dirt, or moisture, periodic cleaning of the components is recommended to prevent the accumulation of contaminants that can accelerate wear of the insert. Additionally, monitoring the operating temperature of the coupling can help detect potential issues—excessive heat may indicate misalignment, overloading, or degradation of the insert material. By addressing these issues promptly, maintenance personnel can minimize downtime and reduce repair costs.
Technological advancements in recent years have led to significant improvements in the design and performance of multi jaw couplings. One of the key areas of innovation is the development of advanced materials for the elastic insert. For example, the use of thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) and composite materials has resulted in inserts that offer higher wear resistance, better temperature stability, and longer service life than traditional rubber or polyurethane inserts. These advanced materials also provide improved resistance to chemicals and UV radiation, expanding the application range of multi jaw couplings to more harsh environments.
Another area of advancement is the optimization of hub design through computer-aided design (CAD) and finite element analysis (FEA). These tools allow engineers to design hubs with more efficient geometries, reducing weight while maintaining or increasing torque capacity. For example, hollow hubs or hubs with optimized rib structures offer improved strength-to-weight ratios, making them suitable for lightweight applications such as electric vehicles. Additionally, advancements in manufacturing processes, such as precision machining and 3D printing, have enabled the production of complex jaw geometries that improve the interface between the hub and the insert, reducing stress concentrations and enhancing torque transmission efficiency.
The integration of smart monitoring technologies is also a growing trend in multi jaw couplings. Modern couplings can be equipped with sensors that measure parameters such as vibration, temperature, and torque. This real-time data is transmitted to a central monitoring system, allowing maintenance personnel to detect early signs of insert wear, misalignment, or overloading. Predictive maintenance based on this data helps to schedule maintenance activities proactively, reducing unplanned downtime and improving the overall reliability of the machinery. Furthermore, the development of modular coupling systems allows for easy replacement of components, such as inserts or hubs, without the need for specialized tools, further reducing maintenance time and costs.
Despite their numerous advantages, multi jaw couplings also have certain limitations that must be considered when selecting a coupling for a specific application. One of the main limitations is their limited misalignment tolerance compared to more flexible couplings, such as rubber tyre couplings or universal joints. This makes them unsuitable for applications with significant shaft misalignments. Another limitation is the temperature range of the elastic insert—most standard inserts can only withstand temperatures between -30°C and 120°C, making them unsuitable for extreme high-temperature or low-temperature applications unless specialized materials are used. Additionally, the elastic insert is susceptible to degradation from exposure to certain chemicals, such as strong acids, bases, or solvents, which can limit their use in chemical processing applications without proper material selection.
In conclusion, multi jaw couplings are a reliable and versatile solution for mechanical power transmission, offering a balanced combination of torque transmission efficiency, misalignment accommodation, vibration damping, and cost-effectiveness. Their modular design, which combines metal hubs with an elastic insert, makes them easy to install, maintain, and replace, contributing to their widespread adoption across industries such as industrial machinery, automotive, food processing, and renewable energy. Material selection plays a crucial role in their performance, with the choice of hub material (steel, stainless steel, aluminum) and insert material (rubber, polyurethane, silicone) tailored to the specific requirements of the application.
Proper installation and regular maintenance are essential to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of multi jaw couplings, with a particular focus on shaft alignment and the inspection of the elastic insert. Recent technological advancements in materials, design, and monitoring systems have further enhanced their capabilities, expanding their application range and improving their reliability. Despite their limitations, multi jaw couplings remain a preferred choice for many critical applications due to their robust performance, simplicity, and cost-effectiveness. As industries continue to evolve and demand more efficient and reliable power transmission systems, multi jaw couplings are likely to undergo further innovations, solidifying their position as a key component in modern mechanical systems. Whether in a small industrial pump, a heavy-duty tractor, or a renewable energy generator, multi jaw couplings play an indispensable role in ensuring the smooth and efficient transfer of power, contributing to the overall productivity and reliability of industrial operations.
« Multi Jaw Couplings » Post Date: 2024/4/25 , https://www.rokeecoupling.net/tags/multi-jaw-couplings.html