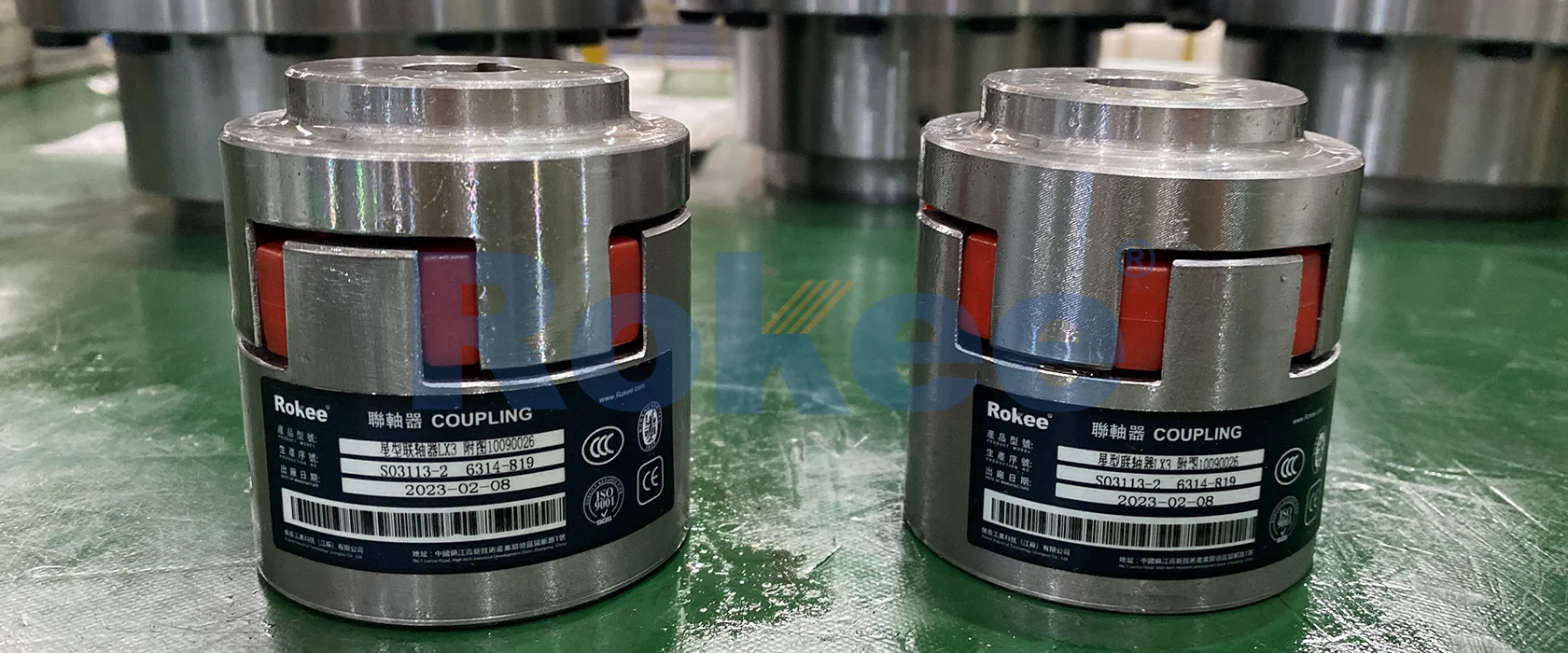

Rokee is a well-known high-quality supplier of Stainless Steel Jaw Couplings and technical services in China, customize stainless steel jaw couplings according to user drawings, alternatively, if the user provides stainless steel jaw couplings parameters, we can select the model and design drawings for you, support wholesale and export.


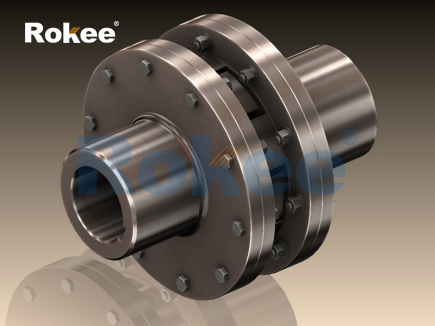

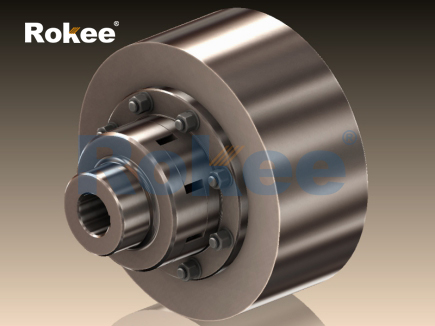


In the realm of mechanical power transmission, couplings serve as indispensable components that bridge the gap between driving and driven shafts, ensuring the smooth transfer of torque and rotational motion. Among the diverse array of coupling types, the stainless steel jaw coupling has emerged as a preferred choice in numerous industrial applications, thanks to its unique combination of structural simplicity, corrosion resistance, and reliable performance. Unlike rigid couplings that demand precise shaft alignment or complex diaphragm couplings designed for high-precision torque transmission, the stainless steel jaw coupling achieves torque transfer and misalignment compensation through the interaction between elastomeric elements and jaw-shaped hubs—all while leveraging the inherent advantages of stainless steel materials. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of the stainless steel jaw coupling, covering its structural composition, working principle, key performance advantages, typical application scenarios, selection criteria, and maintenance practices. The goal is to offer engineering professionals and technical personnel a systematic and in-depth understanding of this versatile transmission component.
The structural design of the stainless steel jaw coupling is characterized by simplicity, robustness, and ease of assembly, consisting of three core components: two stainless steel jaw hubs, an elastomeric insert (also known as a spider), and optional fastening elements (such as set screws, keyways, or clamp collars). The jaw hubs are the primary load-bearing components, meticulously crafted from high-quality stainless steel alloys—commonly 304, 316, or 316L stainless steel. These alloys are selected for their exceptional corrosion resistance, excellent mechanical strength, and good ductility, making them suitable for harsh operating environments where moisture, chemicals, or extreme temperatures are present. Each jaw hub features a series of evenly spaced, protruding "jaws" around its circumference; the number of jaws typically ranges from 3 to 6, depending on the coupling size and torque rating. The inner bore of the hubs is precision-machined to accommodate the driving and driven shafts, with common connection methods including keyway fits, interference fits, or clamp-style connections to ensure a secure, slip-free engagement.
The elastomeric insert is the critical flexible element that distinguishes jaw couplings from rigid alternatives. Positioned between the two jaw hubs, the insert features recesses that perfectly mate with the jaws of the hubs, creating a secure interlocking mechanism. Elastomeric inserts are typically manufactured from durable, flexible materials such as nitrile rubber (NBR), ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), polyurethane (PU), or silicone. The material selection for the insert is tailored to the specific application requirements: NBR offers excellent oil resistance for industrial machinery, EPDM excels in high-temperature and chemical-resistant environments, PU provides superior wear resistance and load-bearing capacity, and silicone is ideal for extreme temperature ranges. The insert not only transmits torque from one hub to the other but also absorbs vibration, dampens shock loads, and compensates for minor shaft misalignments—including axial, radial, and angular displacements. Some advanced designs may incorporate split inserts or replaceable elements, allowing for easy maintenance without disassembling the entire coupling or disconnecting the shafts.
The working principle of the stainless steel jaw coupling revolves around the synergistic interaction between the rigid stainless steel hubs and the flexible elastomeric insert. When the driving shaft rotates, it imparts rotational motion to the driving jaw hub. The jaws of this hub engage with the corresponding recesses in the elastomeric insert, transferring torque to the insert through frictional and mechanical contact. The insert then transmits this torque to the driven jaw hub, which in turn drives the driven shaft. During operation, the elastomeric insert undergoes elastic deformation to accommodate minor shaft misalignments. For axial displacement (relative movement of shafts along their axis), the insert compresses or stretches slightly to absorb the movement without generating excessive axial forces. For radial displacement (offset of shaft centers in the radial direction), the insert bends laterally to bridge the gap between the misaligned jaws. For angular displacement (tilt between the shaft axes), the insert deforms asymmetrically, allowing the hubs to rotate at an angle relative to each other while maintaining torque transmission. Additionally, the elastomeric material acts as a vibration damper, absorbing high-frequency vibrations generated by the driving motor or the driven equipment, thereby reducing noise and minimizing wear on other components in the transmission system.
The stainless steel jaw coupling offers a multitude of performance advantages that make it a versatile and reliable choice for various industrial applications. Firstly, it boasts exceptional corrosion resistance, a direct benefit of its stainless steel construction. Unlike carbon steel couplings that are prone to rust and degradation in humid or corrosive environments, stainless steel jaw couplings can withstand exposure to water, chemicals, saltwater, and industrial gases—making them ideal for outdoor applications, marine environments, and chemical processing plants. Secondly, it provides effective vibration damping and shock absorption. The elastomeric insert acts as a buffer, absorbing shock loads during startup or sudden load changes and reducing vibration transmission between the driving and driven shafts. This not only improves the stability of the equipment but also extends the service life of bearings, seals, and other critical components. Thirdly, it offers excellent misalignment compensation capability. While not designed for extreme misalignments (typically limited to 0.1-0.5 mm radial displacement, 1-3 mm axial displacement, and 1-5 degrees angular displacement, depending on the model), the coupling can accommodate the minor misalignments that are common in practical installation and operation, reducing the need for precise alignment and simplifying installation procedures.
Fourthly, the stainless steel jaw coupling features a compact structure and lightweight design. Its simple composition ensures a small footprint, making it suitable for applications with limited installation space, such as in precision machinery, medical equipment, and automotive components. The lightweight nature of stainless steel (compared to other high-strength alloys) also minimizes inertial forces during operation, improving energy efficiency. Fifthly, it is easy to install and maintain. The modular design allows for quick assembly and disassembly; in most cases, the elastomeric insert can be replaced without removing the hubs from the shafts, significantly reducing downtime for maintenance. Finally, it offers a cost-effective solution for torque transmission. Compared to high-precision couplings (such as diaphragm or disc couplings), stainless steel jaw couplings are more affordable to manufacture and purchase, while still meeting the performance requirements of most general industrial applications. This combination of performance and cost-effectiveness makes them a popular choice for both small-scale and large-scale industrial operations.
Due to its unique performance characteristics, the stainless steel jaw coupling is widely used in a diverse range of industries and applications. One of the most common application areas is the chemical and pharmaceutical industry. In chemical processing plants, pumps, mixers, agitators, and conveyors are often exposed to corrosive chemicals, high humidity, and harsh temperatures. The corrosion resistance of stainless steel jaw couplings ensures reliable operation in these environments, while the vibration damping capability protects sensitive equipment components. In pharmaceutical manufacturing, where cleanliness and hygiene are paramount, stainless steel's smooth, non-porous surface is easy to clean and sterilize, complying with strict industry standards. Another major application field is the marine industry. Marine equipment such as ship propeller shafts, auxiliary pumps, and deck machinery operates in saltwater environments, which are highly corrosive to most metals. Stainless steel jaw couplings resist saltwater corrosion, ensuring long-term reliability and reducing maintenance costs for marine vessels.
The food and beverage industry also relies heavily on stainless steel jaw couplings. Equipment such as food processors, conveyors, bottling machines, and refrigeration units require couplings that are corrosion-resistant, easy to clean, and non-contaminating. Stainless steel meets these requirements, while the elastomeric insert (often made of food-grade materials such as silicone or PU) ensures that no harmful substances leach into the food or beverage products. In the water and wastewater treatment industry, pumps, blowers, and aerators are exposed to water, sewage, and various chemicals. Stainless steel jaw couplings withstand the corrosive effects of these substances, ensuring continuous operation of critical water treatment equipment. Additionally, the coupling is widely used in precision machinery, such as CNC machine tools, robotics, and automation systems. Here, its compact size, lightweight design, and vibration damping capability help maintain the precision and stability of motion control systems.
Other notable applications include the automotive industry (for connecting auxiliary components such as water pumps and alternators), the renewable energy sector (in small wind turbines and solar tracking systems), and the medical equipment industry (in diagnostic machines and laboratory equipment). In each of these applications, the stainless steel jaw coupling's ability to balance performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness makes it an indispensable component of the transmission system.
Selecting the appropriate stainless steel jaw coupling is critical to ensuring the reliable operation of the transmission system, optimizing performance, and minimizing maintenance costs. When making a selection, several key factors should be considered. Firstly, torque requirements. The rated torque of the coupling must be greater than or equal to the maximum operating torque of the system, including startup torque and shock loads. A safety margin of 1.2-2.0 is typically recommended, depending on the severity of the load fluctuations. For example, in applications with frequent startup and shutdown or heavy shock loads (such as crushers or conveyors), a higher safety margin should be adopted. Secondly, shaft misalignment. The coupling's maximum allowable misalignment (axial, radial, angular) must exceed the actual misalignment present in the system. It is important to measure or calculate the expected misalignment during installation and operation, as excessive misalignment can lead to premature failure of the elastomeric insert.
Thirdly, operating environment. The environmental conditions (temperature, humidity, corrosion, dust) directly influence the selection of the stainless steel alloy and the elastomeric insert material. For high-temperature environments (above 100°C), 316 stainless steel and silicone or EPDM inserts are preferred. For corrosive environments (such as chemical plants or marine applications), 316L stainless steel (with enhanced corrosion resistance) is recommended. For food-grade applications, food-safe elastomers (such as FDA-approved silicone or PU) should be selected. Fourthly, shaft size and connection type. The coupling's inner bore must match the diameter of the driving and driven shafts. The connection method (keyway, clamp, interference fit) should be compatible with the shaft design and installation requirements. Clamp-style connections are often preferred for easy installation and removal, while keyway fits provide a more secure connection for high-torque applications.
Fifthly, operating speed. The maximum allowable rotational speed of the coupling must be greater than the operating speed of the shafts. Exceeding the maximum speed can generate excessive centrifugal forces, leading to premature wear of the insert or damage to the hubs. Finally, cost and maintenance requirements. While stainless steel jaw couplings are generally cost-effective, the selection of materials (such as 316 vs. 304 stainless steel) and insert types (replaceable vs. non-replaceable) can affect the initial cost and long-term maintenance expenses. For applications where downtime is costly, replaceable inserts are recommended to minimize maintenance time.
Proper maintenance of the stainless steel jaw coupling is essential to ensure its long-term performance and extend its service life. The maintenance process primarily includes regular inspection, cleaning, lubrication (where necessary), and timely replacement of worn components. Firstly, regular inspection. It is recommended to inspect the coupling periodically (monthly for heavy-duty applications, quarterly for general applications) for signs of wear, damage, or loose connections. Key inspection points include: the condition of the elastomeric insert (cracks, hardening, softening, or excessive wear), the integrity of the stainless steel hubs (corrosion, deformation, or wear on the jaws), and the tightness of fastening elements (set screws, clamp bolts). If any defects are detected, the affected components should be replaced immediately to avoid sudden failure.
Secondly, cleaning. Regular cleaning of the coupling is important, especially in dusty, corrosive, or food-grade environments. The stainless steel hubs can be cleaned using a mild detergent or solvent (compatible with stainless steel) to remove dirt, grease, or chemical residues. The elastomeric insert should be cleaned with a soft brush and mild soap to avoid damage to the material. After cleaning, the coupling should be dried thoroughly to prevent moisture buildup, which can lead to corrosion. Thirdly, lubrication. Most stainless steel jaw couplings do not require lubrication, as the elastomeric insert acts as a self-lubricating element. However, in applications where the insert is exposed to high temperatures or harsh chemicals, a small amount of compatible lubricant (such as silicone grease) can be applied to the insert to reduce friction and extend its life. It is important to avoid using lubricants that are incompatible with the elastomeric material, as this can cause swelling or degradation.
Fourthly, avoiding overload and improper operation. The coupling should be operated within its rated torque and speed limits. Overload operation can cause excessive deformation of the insert, leading to premature failure. Additionally, proper shaft alignment should be maintained to avoid excessive stress on the coupling components. Fifthly, storage and handling. If the coupling is not installed immediately after purchase, it should be stored in a dry, clean, and well-ventilated environment to prevent corrosion. The elastomeric insert should be stored away from direct sunlight, high temperatures, and ozone sources, as these can degrade the material. When handling the coupling, care should be taken to avoid scratching or damaging the stainless steel surfaces, as this can compromise corrosion resistance.
As industrial technology continues to advance, the performance requirements for transmission components such as stainless steel jaw couplings are becoming increasingly stringent. Looking to the future, several development trends are likely to shape the evolution of stainless steel jaw couplings. Firstly, the development of high-performance materials. Advances in stainless steel alloy technology (such as the development of duplex stainless steels or super austenitic stainless steels) will further improve the corrosion resistance, strength, and temperature resistance of coupling hubs. Similarly, innovations in elastomeric materials (such as nanocomposite rubbers or thermoplastic elastomers) will enhance the wear resistance, fatigue life, and environmental adaptability of the insert.
Secondly, structural optimization and lightweight design. With the help of advanced simulation tools (such as finite element analysis) and additive manufacturing technology, manufacturers will be able to optimize the design of the jaw hubs—reducing weight while maintaining strength. Additive manufacturing (3D printing) will also enable the production of complex, customized jaw designs that better accommodate specific application requirements, such as irregular shaft sizes or unique installation constraints. Thirdly, the integration of intelligent monitoring capabilities. The incorporation of sensors (such as strain gauges, temperature sensors, or vibration sensors) into the coupling will enable real-time monitoring of its operating state. This data can be transmitted to a central control system, allowing for predictive maintenance—identifying potential issues (such as insert wear or misalignment) before they lead to failure. This will significantly reduce downtime and improve the reliability of the transmission system.
Fourthly, the development of specialized designs for extreme applications. As industries such as aerospace, deep-sea exploration, and nuclear energy continue to expand, there will be a growing demand for stainless steel jaw couplings that can operate in extreme conditions—such as ultra-high temperatures, ultra-high pressures, or high-radiation environments. Manufacturers will respond by developing specialized designs and material combinations to meet these challenging requirements.
In conclusion, the stainless steel jaw coupling is a versatile and reliable mechanical transmission component that combines the structural simplicity of jaw couplings with the corrosion resistance and durability of stainless steel. Its key advantages—including excellent corrosion resistance, effective vibration damping, reliable misalignment compensation, compact design, and ease of maintenance—make it suitable for a wide range of applications across industries such as chemical processing, marine, food and beverage, water treatment, and precision machinery. The correct selection of the coupling, based on factors such as torque requirements, operating environment, and shaft size, is critical to ensuring optimal performance. Proper maintenance practices, including regular inspection, cleaning, and timely component replacement, will extend the service life of the coupling and minimize downtime.
Looking ahead, the continued development of high-performance materials, structural optimization, intelligent monitoring, and specialized designs will further enhance the capabilities of stainless steel jaw couplings, expanding their application range and improving their reliability in even the most challenging operating conditions. For engineering professionals, a thorough understanding of the stainless steel jaw coupling's characteristics, selection criteria, and maintenance requirements is essential for leveraging this component effectively in practical applications, ultimately improving the performance, efficiency, and reliability of mechanical systems.
« Stainless Steel Jaw Couplings » Post Date: 2024/4/25 , https://www.rokeecoupling.net/tags/stainless-steel-jaw-couplings.html