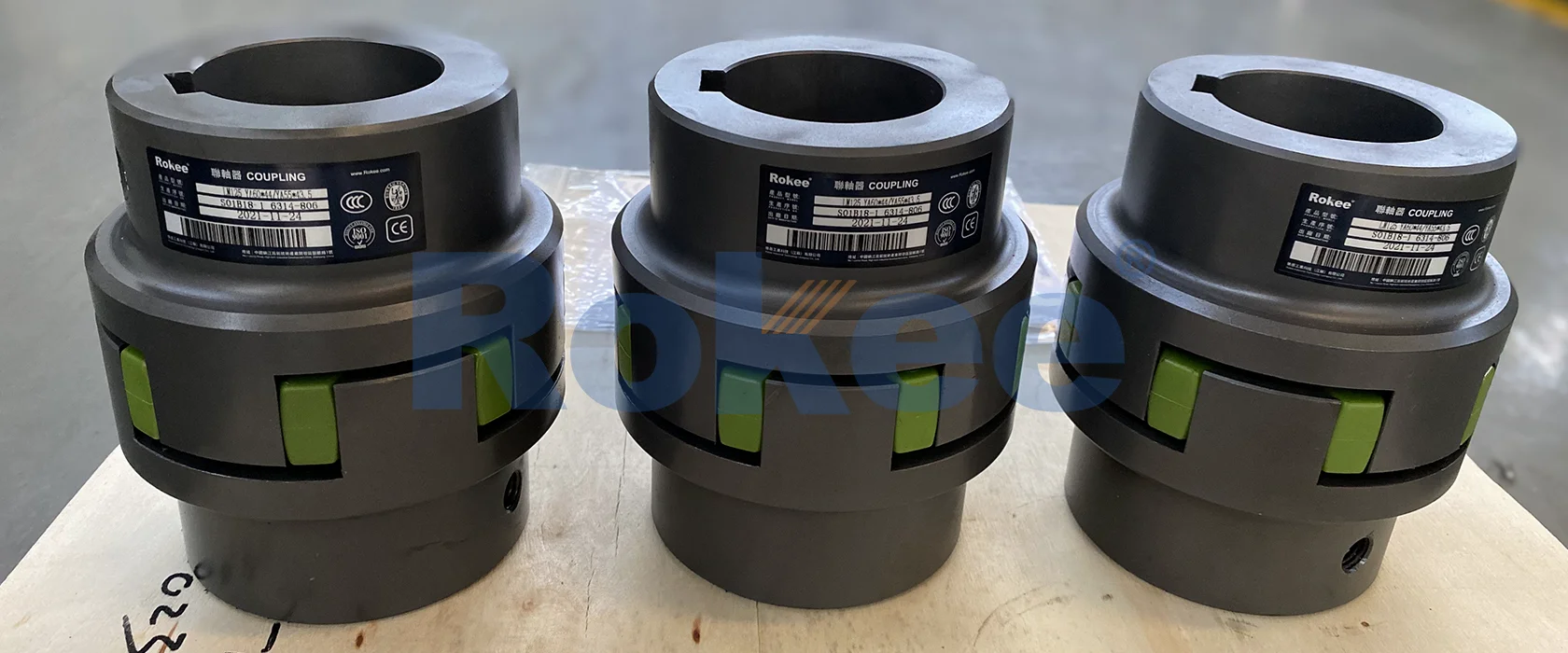

Rokee is a well-known high-quality supplier of Plum-shaped Couplings and technical services in China, customize plum-shaped couplings according to user drawings, alternatively, if the user provides plum-shaped couplings parameters, we can select the model and design drawings for you, support wholesale and export.


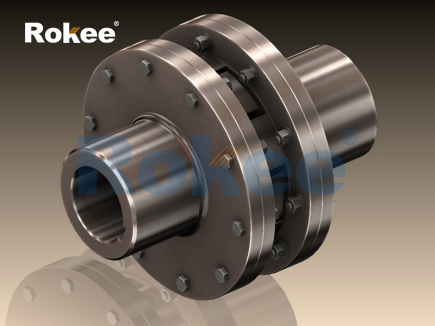

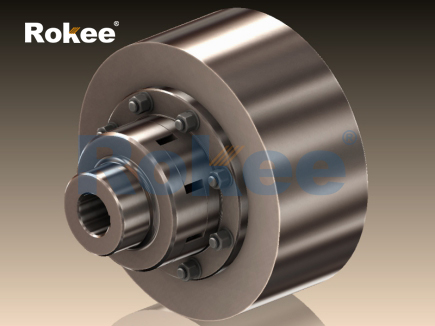


In the domain of mechanical power transmission, couplings play a pivotal role in establishing a secure and efficient connection between rotating shafts, facilitating torque transfer while addressing challenges such as misalignment, vibration, and shock loads. Among the diverse array of flexible couplings, the plum-shaped coupling—also known as the jaw coupling with a plum rubber element—stands out for its compact structure, reliable performance, and excellent damping capabilities. Leveraging a unique plum-shaped elastic component to bridge two jaw-shaped hubs, this coupling type has become a preferred choice in numerous industrial, automotive, and agricultural applications. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of plum-shaped couplings, covering their structural design, working mechanism, material selection criteria, diverse application scenarios, key advantages, maintenance protocols, and future development trends. By delving into these aspects, we aim to offer a thorough understanding of this essential mechanical component and its significance in ensuring the smooth and reliable operation of rotating machinery.
A plum-shaped coupling is a type of flexible elastic coupling specifically designed to transmit torque between two coaxial shafts while accommodating moderate levels of misalignment and absorbing vibrations. Its defining feature is the plum-shaped rubber (or elastic) element, which is inserted between two symmetrically designed jaw-shaped metal hubs. Unlike rigid couplings that demand precise shaft alignment and lack vibration absorption capabilities, plum-shaped couplings are engineered to handle three primary types of misalignment: axial (linear movement along the shaft axis), radial (offset between the centers of the two shafts), and angular (tilt between the shaft axes). This flexibility, combined with effective vibration damping, makes plum-shaped couplings well-suited for applications where operational smoothness and component protection are paramount.
The structural composition of a plum-shaped coupling is relatively simple yet robust, consisting of three core components: two metal jaw hubs, a plum-shaped elastic element, and fastening hardware (such as bolts, nuts, or set screws). The metal jaw hubs are the primary load-bearing components, responsible for connecting the coupling to the driving and driven shafts and transmitting torque to the elastic element. These hubs are typically designed with a series of evenly spaced jaws (usually 3 to 6 jaws, depending on the size and torque capacity) that mesh with the lobes of the plum-shaped elastic element. To ensure a secure connection with the shafts, the hubs are often equipped with keyways, set screws, or shrink-fit designs. Keyways allow for the insertion of a key that prevents relative rotation between the hub and the shaft, while set screws provide additional locking force to enhance stability.
The plum-shaped elastic element—often referred to as the "plum blossom" element due to its petal-like lobes—is the heart of the coupling. This element is typically cylindrical in overall shape, with several radially extending lobes (corresponding to the number of jaws on the hubs) that fit snugly into the gaps between the jaws of the two hubs. The number of lobes can vary, but 3-lobe, 4-lobe, and 6-lobe designs are the most common, with more lobes generally enabling higher torque transmission and more uniform force distribution. The elastic element may also feature a central hole or sleeve to accommodate a bolt or pin that helps align and secure the two hubs, preventing axial displacement during operation.
While the basic structure of plum-shaped couplings is consistent, there are several design variations tailored to specific application requirements. One common variation is the split plum-shaped coupling, where the metal hubs are split into two halves, allowing for easy installation and replacement without the need to disconnect the shafts or move the connected machinery. This design is particularly advantageous in tight spaces or in applications where minimizing downtime is critical. Another variation is the reinforced plum-shaped coupling, which features thicker hub walls or additional ribbing to enhance torque capacity, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Additionally, some designs incorporate polyurethane or other high-performance elastic materials instead of rubber for the plum element, offering improved wear resistance and temperature tolerance.
The working principle of a plum-shaped coupling revolves around the elastic deformation of the plum-shaped element. When torque is applied to the driving shaft, the corresponding jaw hub rotates, and the jaws of the hub exert a force on the lobes of the plum-shaped elastic element. This force causes the elastic element to undergo controlled torsional deformation—twisting slightly as it transfers the torque to the lobes in contact with the driven hub. As the driven hub rotates, the torque is transmitted to the driven shaft, completing the power transmission process.
A key aspect of the working mechanism is the coupling’s ability to accommodate misalignment. When the shafts are misaligned (due to factors such as installation errors, thermal expansion, or shaft deflection), the plum-shaped elastic element flexes to bridge the gap between the two hubs. For angular misalignment, the lobes of the elastic element bend slightly to allow the two shafts to operate at an angle; for radial misalignment, the element stretches or compresses to compensate for the offset between the shaft centers; and for axial misalignment, the element expands or contracts along the shaft axis. This flexibility ensures that excessive stress is not transferred to the shafts, bearings, or other connected components, reducing wear and extending their service life.
Another critical function of the plum-shaped element is vibration damping. As the coupling operates, the rotating machinery generates vibrational energy, which is transmitted to the elastic element. The rubber or polyurethane material of the element absorbs this energy through deformation and dissipates it as heat, reducing the amplitude of vibrations transferred to the driven shaft and equipment. This damping effect not only reduces operational noise but also protects sensitive components (such as motors, pumps, or gearboxes) from damage caused by excessive vibration or shock loads—such as those occurring during sudden start-ups, shutdowns, or load fluctuations.
Material selection is a decisive factor in determining the performance, durability, and application scope of plum-shaped couplings. The choice of materials for each component is guided by factors such as torque requirements, operating temperature, environmental conditions (e.g., humidity, chemical exposure), and load type (steady or intermittent).
The metal jaw hubs are typically manufactured from high-strength metals to withstand the mechanical stresses of torque transmission. Carbon steel is the most common material for general-purpose applications, offering a balance of strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness. For applications requiring higher torque capacity or enhanced fatigue resistance (such as heavy-duty industrial machinery), alloy steels (e.g., chromium-molybdenum steel) are preferred. These alloy steels are often heat-treated (quenched and tempered) to improve their hardness, tensile strength, and resistance to wear. In corrosive environments (such as marine or chemical processing applications), stainless steel hubs may be used to prevent rust and degradation.
The plum-shaped elastic element is most commonly made from rubber or polyurethane. Natural rubber is used for general-purpose applications due to its excellent elasticity, good damping properties, and low cost. However, natural rubber has limitations: it is susceptible to degradation at high temperatures (above 80°C), and it may be damaged by exposure to oils, greases, or chemicals. For applications involving lubricants or harsh industrial fluids, nitrile rubber (NBR) is preferred, as it exhibits excellent oil and fuel resistance. Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) rubber is suitable for outdoor applications or high-temperature environments (up to 150°C), as it offers superior resistance to ozone, weathering, and high temperatures. Polyurethane is another popular material for the plum element, providing higher wear resistance, better load-bearing capacity, and a wider temperature range (-40°C to 120°C) compared to rubber. Polyurethane elements also have a longer service life in applications with high levels of friction or abrasion.
Fastening hardware (bolts, nuts, set screws) is typically made from stainless steel or high-strength carbon steel to ensure secure locking and resistance to corrosion. In applications where vibration may cause loosening, lock washers or thread-locking compounds may be used to enhance the stability of the fasteners.
Plum-shaped couplings are widely utilized across a diverse range of industries, thanks to their compact size, reliable performance, and versatility. One of the largest application areas is the industrial machinery sector, where they are used to connect motors to a wide range of equipment, including pumps, compressors, fans, conveyors, mixers, agitators, and gearboxes. In centrifugal pump systems, for example, plum-shaped couplings compensate for minor misalignments between the motor and pump shafts, reducing the risk of bearing failure and improving the overall reliability of the system. In conveyor systems, which are often subject to intermittent shock loads and minor misalignments, the coupling’s damping capabilities absorb vibrations and ensure smooth torque transmission, minimizing downtime.
The automotive industry is another major user of plum-shaped couplings. They are employed in various components, including drive shafts, steering systems, and auxiliary equipment such as water pumps, alternators, and air conditioning compressors. In automotive drive shafts, the coupling’s compact size and vibration damping properties help reduce noise and improve ride comfort. In steering systems, it absorbs shocks from the road surface, enhancing steering precision and reducing driver fatigue. Additionally, plum-shaped couplings are used in electric vehicles (EVs) to connect electric motors to transmissions or reducers, where their ability to handle high torque and reduce vibration is critical for the efficiency and reliability of the powertrain.
The agricultural industry relies heavily on plum-shaped couplings for farming equipment such as tractors, harvesters, irrigation pumps, and tillers. Agricultural machinery operates in harsh environments—characterized by dust, dirt, vibration, and variable loads—and the coupling’s robust design and ability to withstand these conditions make it well-suited for such applications. For example, in tractor power take-off (PTO) systems, plum-shaped couplings connect the tractor’s engine to implements (e.g., plows, mowers, balers), accommodating misalignment caused by uneven terrain and absorbing shock loads during operation.
Other key application areas include the food and beverage industry, where plum-shaped couplings are used in processing equipment (e.g., mixers, blenders, conveyors) due to their easy maintenance and ability to prevent contamination (some designs use food-grade elastic materials); the pharmaceutical industry, where they are employed in equipment requiring precise torque transmission and low vibration (e.g., tablet presses, mixers); and the renewable energy sector, particularly in small to medium-sized wind turbines and solar tracking systems, where they connect the rotor or motor to the generator, accommodating misalignment caused by wind loads or structural movement.
Plum-shaped couplings offer several distinct advantages that make them a preferred choice over other coupling types (such as rigid couplings, metallic flexible couplings, or tire couplings) in many applications. One of the most significant advantages is their compact and lightweight design. Compared to larger flexible couplings (e.g., tire couplings), plum-shaped couplings occupy less space, making them ideal for applications where installation space is limited—such as in compact industrial machinery, automotive components, or portable equipment.
Excellent vibration damping and shock absorption capabilities are another key advantage. The plum-shaped elastic element acts as a buffer, absorbing vibrational energy and reducing the transmission of shocks to the connected machinery. This not only reduces operational noise but also minimizes wear and tear on bearings, seals, and other components, extending the service life of the entire system. This is particularly beneficial in applications with frequent start-ups, shutdowns, or variable loads, where shock loads are common.
Plum-shaped couplings also excel at accommodating moderate levels of misalignment. While they may not handle as much misalignment as larger tire couplings, they can effectively compensate for the minor to moderate axial, radial, and angular misalignments commonly encountered in most industrial applications. This reduces the need for precise and time-consuming shaft alignment during installation, simplifying the setup process and reducing maintenance requirements.
Ease of installation and maintenance is another major advantage. Most plum-shaped couplings feature a simple design that allows for quick and easy installation—many split-hub designs can be installed without disconnecting the shafts, significantly reducing downtime. Replacing the plum-shaped elastic element is also straightforward: simply remove the fastening hardware, extract the old element, and insert a new one. This simplicity reduces maintenance costs and ensures that the coupling can be quickly returned to service.
Cost-effectiveness is an additional benefit. Plum-shaped couplings are generally less expensive to manufacture than complex metallic flexible couplings (e.g., disc couplings) or large tire couplings. Their simple design, fewer components, and ease of maintenance further contribute to their cost-effectiveness over the long term. For many general-purpose applications, they offer an optimal balance of performance and cost.
Despite their numerous advantages, plum-shaped couplings require proper maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Regular inspection is the foundation of effective maintenance, as it allows for the early detection of potential issues before they lead to coupling failure or damage to connected equipment. Operators should inspect the coupling regularly (the frequency depending on the operating conditions and application) for signs of wear or damage to the plum-shaped elastic element, such as cracks, tears, hardening, swelling, or excessive wear on the lobes. These signs indicate that the element is deteriorating and should be replaced promptly to avoid loss of flexibility, reduced damping capacity, or complete coupling failure.
The metal jaw hubs should also be inspected regularly for signs of damage, such as cracks, deformation, or wear on the jaw surfaces. Loose fastening hardware (bolts, set screws) is another common issue that should be addressed immediately, as it can lead to excessive vibration, misalignment, or even disconnection of the coupling during operation. Additionally, operators should check for corrosion on the metal components, especially in humid or corrosive environments, and take appropriate measures (e.g., applying anti-corrosion coatings) to prevent further degradation.
Lubrication requirements for plum-shaped couplings are minimal compared to other coupling types. Most designs do not require lubrication for the elastic element, as the rubber or polyurethane material acts as a self-lubricating surface. However, if the coupling features metal-to-metal contact points (e.g., between the hub and the shaft), these areas may require periodic lubrication to reduce friction and prevent wear. When lubrication is necessary, it is critical to use a lubricant that is compatible with the elastic element material—some petroleum-based lubricants can degrade rubber, leading to premature failure. Silicone-based or synthetic lubricants are generally recommended for use with rubber or polyurethane components.
Replacement of the plum-shaped elastic element is the most common maintenance procedure. When replacing the element, it is essential to select a replacement that matches the original specifications, including material, size, number of lobes, and torque capacity. Using an incompatible element can reduce the coupling’s performance, increase the risk of failure, and potentially damage the connected machinery. The replacement process typically involves the following steps: 1) Remove the fastening hardware (bolts, nuts) that secure the two hubs together; 2) Separate the hubs slightly to extract the old elastic element; 3) Insert the new element, ensuring that the lobes are properly aligned with the jaws of both hubs; 4) Reattach the hubs and tighten the fastening hardware to the recommended torque. It is important to ensure that the new element is seated correctly to avoid misalignment or uneven load distribution.
Proper storage of plum-shaped couplings (when not in use) is also important to prevent premature degradation of the elastic element. Couplings should be stored in a cool, dry, and clean environment, away from direct sunlight, ozone sources (e.g., electrical motors), and chemicals that can degrade rubber or polyurethane. Storing couplings in a compressed or deformed state should be avoided, as this can cause permanent damage to the elastic element. Additionally, metal components should be protected from moisture to prevent corrosion.
Looking ahead, the development of plum-shaped couplings is being driven by the increasing demand for more efficient, reliable, and sustainable mechanical systems. One of the key trends in the industry is the development of high-performance elastic materials for the plum-shaped element. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to create rubber and polyurethane compounds with enhanced properties, such as higher temperature resistance, improved wear resistance, greater torque capacity, and longer service life. For example, the use of nanocomposite materials—rubber or polyurethane reinforced with nanoparticles (e.g., carbon nanotubes, silica)—is being explored to improve the mechanical strength and durability of the elastic element while maintaining its excellent damping properties. These advanced materials will enable plum-shaped couplings to be used in more demanding applications, such as high-temperature industrial processes or heavy-duty machinery.
Another emerging trend is the integration of smart technologies into plum-shaped couplings. The development of smart couplings equipped with sensors (e.g., strain gauges, temperature sensors, vibration sensors) that monitor torque, temperature, vibration, and the condition of the elastic element is gaining momentum. These sensors provide real-time data on the coupling’s operating conditions, allowing operators to implement predictive maintenance strategies. By detecting early signs of wear or damage (e.g., changes in vibration patterns, increased temperature, or reduced torque transmission efficiency), predictive maintenance can reduce downtime, improve reliability, and lower maintenance costs. Additionally, the data collected by these sensors can be integrated into industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) systems, enabling remote monitoring and control of the coupling and connected machinery.
Miniaturization is another important trend, driven by the growing demand for compact machinery in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics. Manufacturers are developing smaller, lighter plum-shaped couplings that can transmit high levels of torque while occupying less space. This requires the use of advanced materials (e.g., lightweight alloy steels, high-strength polyurethane) and precision manufacturing techniques (e.g., CNC machining) to ensure that the miniaturized couplings maintain the same level of performance and reliability as their larger counterparts. Miniaturized plum-shaped couplings are particularly important for electric vehicles, portable industrial equipment, and small-scale automation systems, where space and weight are critical constraints.
Environmental sustainability is also shaping the future of plum-shaped couplings. Manufacturers are focusing on reducing the environmental impact of their products by using eco-friendly materials (e.g., recycled rubber, bio-based polyurethane) and implementing sustainable manufacturing processes. Recycled rubber, made from discarded tires and other rubber products, is being used to produce the plum-shaped element, reducing waste and conserving natural resources. Bio-based polyurethane, derived from renewable sources (e.g., plant oils), offers a more sustainable alternative to petroleum-based polyurethane. Additionally, manufacturers are designing couplings with longer service lives and easier recyclability, further reducing their environmental footprint.
In conclusion, plum-shaped couplings are essential components in mechanical power transmission systems, offering a unique combination of compact design, reliable torque transmission, excellent vibration damping, and ease of maintenance. Their ability to accommodate moderate misalignments, protect connected equipment from shock loads, and operate efficiently in a wide range of environments makes them suitable for numerous applications across industries such as industrial machinery, automotive, agriculture, food processing, and renewable energy. Proper material selection and regular maintenance are critical to ensuring their optimal performance and longevity. Looking forward, the development of advanced elastic materials, smart technologies, miniaturization, and sustainable design will continue to enhance the capabilities of plum-shaped couplings, making them even more versatile and reliable. As mechanical systems become increasingly complex and demanding, plum-shaped couplings will remain a vital component in ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of rotating machinery.
« Plum-shaped Couplings » Post Date: 2024/4/25 , https://www.rokeecoupling.net/tags/plum-shaped-couplings.html